Structure of the Plasmodium falciparum M17 aminopeptidase and significance for the design of drugs targeting the neutral exopeptidases
- PMID: 20133789
- PMCID: PMC2809755
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911813107
Structure of the Plasmodium falciparum M17 aminopeptidase and significance for the design of drugs targeting the neutral exopeptidases
Abstract
Current therapeutics and prophylactics for malaria are under severe challenge as a result of the rapid emergence of drug-resistant parasites. The human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum expresses two neutral aminopeptidases, PfA-M1 and PfA-M17, which function in regulating the intracellular pool of amino acids required for growth and development inside the red blood cell. These enzymes are essential for parasite viability and are validated therapeutic targets. We previously reported the X-ray crystal structure of the monomeric PfA-M1 and proposed a mechanism for substrate entry and free amino acid release from the active site. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structure of the hexameric leucine aminopeptidase, PfA-M17, alone and in complex with two inhibitors with antimalarial activity. The six active sites of the PfA-M17 hexamer are arranged in a disc-like fashion so that they are orientated inwards to form a central catalytic cavity; flexible loops that sit at each of the six entrances to the catalytic cavern function to regulate substrate access. In stark contrast to PfA-M1, PfA-M17 has a narrow and hydrophobic primary specificity pocket which accounts for its highly restricted substrate specificity. We also explicate the essential roles for the metal-binding centers in these enzymes (two in PfA-M17 and one in PfA-M1) in both substrate and drug binding. Our detailed understanding of the PfA-M1 and PfA-M17 active sites now permits a rational approach in the development of a unique class of two-target and/or combination antimalarial therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
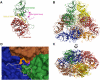
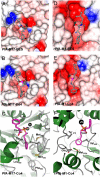
 ) is shown as a black sphere and is labeled. (B, C) Cartoon diagrams of the biologically functional PfA-M17 hexamer colored by chain: A (Green); B (Blue); C (Red); D (Yellow) E (Orange) F (Brown). The six active sites line an interior cavity. (D) The molecular surface of
) is shown as a black sphere and is labeled. (B, C) Cartoon diagrams of the biologically functional PfA-M17 hexamer colored by chain: A (Green); B (Blue); C (Red); D (Yellow) E (Orange) F (Brown). The six active sites line an interior cavity. (D) The molecular surface of  by chain (as colored in (B, C). The active site zinc and carbonate of chain B are visible (Purple spheres). Chains C & D are occluded in this view. The position of the loop (with the molecular surface omitted) in chain B that sits at the entrance to the catalytic cavity is shown by yellow coil (residues 246-265). This region is disordered in the other chains.
by chain (as colored in (B, C). The active site zinc and carbonate of chain B are visible (Purple spheres). Chains C & D are occluded in this view. The position of the loop (with the molecular surface omitted) in chain B that sits at the entrance to the catalytic cavity is shown by yellow coil (residues 246-265). This region is disordered in the other chains.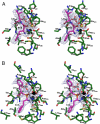
Similar articles
-
Active site metals mediate an oligomeric equilibrium in Plasmodium M17 aminopeptidases.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100173. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016313. Epub 2020 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33303633 Free PMC article.
-
Potent dual inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum M1 and M17 aminopeptidases through optimization of S1 pocket interactions.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Mar 3;110:43-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.015. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26807544
-
X-ray crystal structures of an orally available aminopeptidase inhibitor, Tosedostat, bound to anti-malarial drug targets PfA-M1 and PfA-M17.Proteins. 2015 Apr;83(4):789-95. doi: 10.1002/prot.24771. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 25645579
-
Plasmodium falciparum neutral aminopeptidases: new targets for anti-malarials.Trends Biochem Sci. 2010 Jan;35(1):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010. PMID: 19796954 Review.
-
Metalloaminopeptidases of the Protozoan Parasite Plasmodium falciparum as Targets for the Discovery of Novel Antimalarial Drugs.J Med Chem. 2021 Feb 25;64(4):1763-1785. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01721. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33534577 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphinic Peptides as Tool Compounds for the Study of Pharmacologically Relevant Zn-Metalloproteases.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Nov 28;5(12):1228-1253. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00183. eCollection 2022 Dec 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36524013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Plasmodium falciparum malaria M1 alanyl aminopeptidase (PfA-M1): insights of catalytic mechanism and function from MD simulations.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028589. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22205955 Free PMC article.
-
On-target, dual aminopeptidase inhibition provides cross-species antimalarial activity.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0096624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00966-24. Epub 2024 May 8. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38717141 Free PMC article.
-
Plant leucine aminopeptidases moonlight as molecular chaperones to alleviate stress-induced damage.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 25;287(22):18408-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309500. Epub 2012 Apr 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22493451 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of plasmodial aminopeptidase: a combined molecular docking and QSAR-based in silico approaches.Mol Divers. 2019 Nov;23(4):965-984. doi: 10.1007/s11030-019-09921-y. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Mol Divers. 2019. PMID: 30730017
References
-
- Enserink M. Malaria. Signs of drug resistance rattle experts, trigger bold plan. Science. 2008;322(5909):1776. - PubMed
-
- D’Alessandro U. Existing antimalarial agents and malaria-treatment strategies. Expert Opin Pharmaco. 2009;10(8):1291–1306. - PubMed
-
- Serwold T, Gonzalez F, Kim J, Jacob R, Shastri N. ERAAP customizes peptides for MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 2002;419(6906):480–483. - PubMed
-
- Skinner-Adams TS, et al. Identification of phosphinate dipeptide analog inhibitors directed against the Plasmodium falciparum M17 leucine aminopeptidase as lead antimalarial compounds. J Med Chem. 2007;50(24):6024–6031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

