A selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone
- PMID: 20133810
- PMCID: PMC2823863
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913572107
A selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone
Abstract
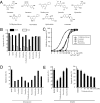
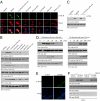
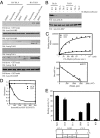
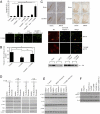
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a cognate ligand for the tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB) receptor, mediates neuronal survival, differentiation, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis. However, BDNF has a poor pharmacokinetic profile that limits its therapeutic potential. Here we report the identification of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone as a bioactive high-affinity TrkB agonist that provokes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone protected wild-type, but not TrkB-deficient, neurons from apoptosis. Administration of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone to mice activated TrkB in the brain, inhibited kainic acid-induced toxicity, decreased infarct volumes in stroke in a TrkB-dependent manner, and was neuroprotective in an animal model of Parkinson disease. Thus, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone imitates BDNF and acts as a robust TrkB agonist, providing a powerful therapeutic tool for the treatment of various neurological diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:381–391. - PubMed
-
- Lindholm D, Dechant G, Heisenberg CP, Thoenen H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a survival factor for cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons and protects them against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5:1455–1464. - PubMed
-
- Schäbitz WR, et al. Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size and counterregulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression after temporary focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2000;31:2212–2217. - PubMed
-
- Askanas V. Neurotrophic factors and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Adv Neurol. 1995;68:241–244. - PubMed
-
- Siegel GJ, Chauhan NB. Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease brain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000;33:199–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

