Hypoxic regulation of nucleus pulposus cell survival: from niche to notch
- PMID: 20133815
- PMCID: PMC2843446
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090734
Hypoxic regulation of nucleus pulposus cell survival: from niche to notch
Abstract
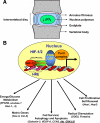
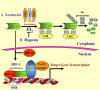
This minireview examines the role of hypoxia, and hypoxia inducible factors (HIF-1 and HIF-2), in regulating the metabolism, function, and fate of cells of the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral disk. We focus on the mechanisms by which both these hypoxia-sensitive transcription factors influence energy metabolism, radical dismutation, and expression of survival proteins. In addition, we discuss how cells of the nucleus respond to a number of hypoxia-sensitive proteins, including galectin-3, Akt, and VEGF. Where applicable, these discussions are extended to include the impact of these molecules and hypoxia on degenerating resident cells in the intervertebral niche. Finally, because the notch signaling pathway is responsive to hypoxia, we speculate that in the intervertebral niche, notch proteins participate in the regulation of disk precursor cell proliferation and differentiation. We predict that knowledge of each of these interactive proteins within the disk niche could be used to enhance renewal and promote differentiation and function of cells of the nucleus pulposus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cited2 modulates hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in nucleus pulposus cells of the rat intervertebral disc.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Dec;58(12):3798-808. doi: 10.1002/art.24073. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 19035510
-
HIF-1 alpha is a regulator of galectin-3 expression in the intervertebral disc.J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Dec;22(12):1851-61. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070620. J Bone Miner Res. 2007. PMID: 17592963
-
A macrophage-dominant PI3K isoform controls hypoxia-induced HIF1α and HIF2α stability and tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Oct;12(10):1520-31. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0682. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25103499
-
Carrot and stick: HIF-alpha engages c-Myc in hypoxic adaptation.Cell Death Differ. 2008 Apr;15(4):672-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402302. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18188166 Review.
-
Nesting and fate of transplanted stem cells in hypoxic/ischemic injured tissues: The role of HIF1α/sirtuins and downstream molecular interactions.Biofactors. 2023 Jan;49(1):6-20. doi: 10.1002/biof.1674. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Biofactors. 2023. PMID: 32939878 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue Engineering Strategies for Intervertebral Disc Treatment Using Functional Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2019 May 13;11(5):872. doi: 10.3390/polym11050872. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31086085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspective on Intradiscal Therapies for Lumbar Discogenic Pain: State of the Science, Knowledge Gaps, and Imperatives for Clinical Adoption.J Pain Res. 2024 Mar 18;17:1171-1182. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S441180. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38524692 Free PMC article.
-
Immune exposure: how macrophages interact with the nucleus pulposus.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1155746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155746. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PHD3 is a transcriptional coactivator of HIF-1α in nucleus pulposus cells independent of the PKM2-JMJD5 axis.FASEB J. 2017 Sep;31(9):3831-3847. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601291R. Epub 2017 May 11. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28495754 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/Akt pathway: a critical player in intervertebral disc degeneration.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(34):57870-57881. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18628. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J, Menage J. Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:10–14. - PubMed
-
- Gruber HE, Ashraf N, Kilburn J, Williams C, Norton HJ, Gordon BE, Hanley EN., Jr Vertebral endplate architecture and vascularization: application of micro-computerized tomography, a vascular tracer, and immunocytochemistry in analyses of disc degeneration in the aging sand rat. Spine. 2005;30:2593–2600. - PubMed
-
- Hassler O. The human intervertebral disc: A micro-angiographical study on its vascular supply at various ages. Acta Orthop Scand. 1969;40:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Rudert M, Tillmann B. Lymph and blood supply of the human intervertebral disc: cadaver study of correlations to discitis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Bartels EM, Fairbank JC, Winlove CP, Urban JP. Oxygen and lactate concentrations measured in vivo in the intervertebral discs of patients with scoliosis and back pain. Spine. 1998;23:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

