Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates myoendothelial junction formation
- PMID: 20133900
- PMCID: PMC2848897
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.215723
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates myoendothelial junction formation
Abstract
Rationale: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is a biomarker for several vascular disease states; however, its target of action within the vessel wall is undefined.
Objective: Determine the ability of PAI-1 to regulate myoendothelial junction (MEJ) formation.
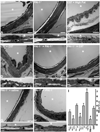
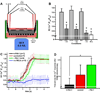
Methods and results: MEJs are found throughout the vasculature linking endothelial cells (ECs) and vascular smooth muscle cells. Using a vascular cell coculture we isolated MEJ fractions and performed two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis. Mass spectrometry identified PAI-1 as being enriched within MEJ fractions, which we confirmed in vivo. In the vascular cell coculture, recombinant PAI-1 added to the EC monolayer significantly increased MEJs. Conversely, addition of a PAI-1 monoclonal antibody to the EC monolayer reduced the number of MEJs. This was also observed in vivo where mice fed a high fat diet had increased PAI-1 and MEJs and the number of MEJs in coronary arterioles of PAI-1(-/-) mice was significantly reduced when compared to C57Bl/6 mice. The presence of MEJs in PAI-1(-/-) coronary arterioles was restored when their hearts were transplanted into and exposed to the circulation of C57Bl/6 mice. Application of biotin-conjugated PAI-1 to the EC monolayer in vitro confirmed the ability of luminal PAI-1 to translocate to the MEJ. Functionally, phenylephrine-induced heterocellular calcium communication in the vascular cell coculture was temporally enhanced when recombinant PAI-1 was present, and prolonged when PAI-1 was absent.
Conclusion: Our data implicate circulating PAI-1 as a key regulator of MEJ formation and a potential target for pharmacological intervention in diseases with vascular abnormalities (eg, diabetes mellitus).
Figures
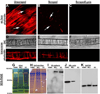
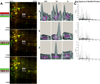
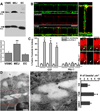
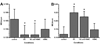

Comment in
-
Regulation of myoendothelial junction formation: bridging the gap.Circ Res. 2010 Apr 2;106(6):1014-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.217786. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20360262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alessi MC, Juhan-Vague I. Metabolic syndrome, haemostasis and thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:995–1000. - PubMed
-
- Lijnen HR. Pleiotropic functions of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Eddy AA, Giachelli CM. Renal expression of genes that promote interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in rats with protein-overload proteinuria. Kidney Int. 1995;47:1546–1557. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T, Kashiwazaki K, Moritomo Y, Nagano S, Adachi M. Albuminuria is directly associated with increased plasma PAI-1 and factor VII levels in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997;36:11–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

