Synchrony with shunting inhibition in a feedforward inhibitory network
- PMID: 20135213
- PMCID: PMC3005186
- DOI: 10.1007/s10827-009-0210-2
Synchrony with shunting inhibition in a feedforward inhibitory network
Abstract
Recent experiments have shown that GABA(A) receptor mediated inhibition in adult hippocampus is shunting rather than hyperpolarizing. Simulation studies of realistic interneuron networks with strong shunting inhibition have been demonstrated to exhibit robust gamma band (20-80 Hz) synchrony in the presence of heterogeneity in the intrinsic firing rates of individual neurons in the network. In order to begin to understand how shunting can contribute to network synchrony in the presence of heterogeneity, we develop a general theoretical framework using spike time response curves (STRC's) to study patterns of synchrony in a simple network of two unidirectionally coupled interneurons (UCI network) interacting through a shunting synapse in the presence of heterogeneity. We derive an approximate discrete map to analyze the dynamics of synchronous states in the UCI network by taking into account the nonlinear contributions of the higher order STRC terms. We show how the approximate discrete map can be used to successfully predict the domain of synchronous 1:1 phase locked state in the UCI network. The discrete map also allows us to determine the conditions under which the two interneurons can exhibit in-phase synchrony. We conclude by demonstrating how the information from the study of the discrete map for the dynamics of the UCI network can give us valuable insight into the degree of synchrony in a larger feed-forward network of heterogeneous interneurons.
Figures

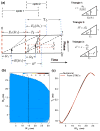
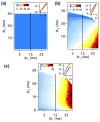
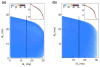




References
-
- Abarbanel H, Gibb L, Huerta R, Rabinovich M. Biophysical model of synaptic plasticity dynamics. Biological Cybernetics. 2003;89:214–226. - PubMed
-
- Acker C, Kopell N, White J. Synchronization of strongly coupled excitatory neurons:relating network behavior to biophysics. Journal of Computational Neuroscience. 2004;15:71–90. - PubMed
-
- Aoki F. Increased gamma-range activity in human sensorimotor cortex during performance of visuomotor tasks. Clinical Neurophysiology. 1999;110:524–537. - PubMed
-
- Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P. Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2007;8:45–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

