Hypoxia influences the vascular expansion and differentiation of embryonic stem cell cultures through the temporal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in an ARNT-dependent manner
- PMID: 20135683
- PMCID: PMC2989499
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.316
Hypoxia influences the vascular expansion and differentiation of embryonic stem cell cultures through the temporal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in an ARNT-dependent manner
Abstract
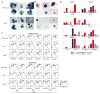
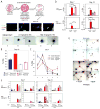
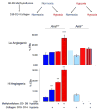
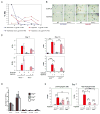
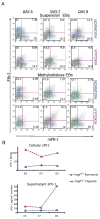
Adaptive responses to low oxygen (O(2)) tension (hypoxia) are mediated by the heterodimeric transcription factor hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). When stabilized by hypoxia, bHLH-PAS alpha- and beta- (HIF-1beta or ARNT) HIF complex regulate the expression of multiple genes, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). To investigate the mechanism(s) through which hypoxia contributes to blood vessel development, we used embryonic stem cell (ESC) differentiation cultures that develop into embryoid bodies (EBs) mimicking early embryonic development. Significantly, low O(2) levels promote vascular development and maturation in wild-type (WT) ESC cultures measured by an increase in the numbers of CD31(+) endothelial cells (ECs) and sprouting angiogenic EBs, but refractory in Arnt(-/-) and Vegf(-/-) ESC cultures. Thus, we propose that hypoxia promotes the production of ECs and contributes to the development and maturation of vessels. Our findings further demonstrate that hypoxia alters the temporal expression of VEGF receptors Flk-1 (VEGFR-2) and the membrane and soluble forms of the antagonistic receptor Flt-1 (VEGFR-1). Moreover, these receptors are distinctly expressed in differentiating Arnt(-/-) and Vegf(-/-) EBs. These results support existing models in which VEGF signaling is tightly regulated during specific biologic events, but also provide important novel evidence that, in response to physiologic hypoxia, HIF mediates a distinct stoichiometric pattern of VEGF receptors throughout EB differentiation analogous to the formation of vascular networks during embryogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda) 2009;24:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez-Bergeron DL, Runge A, Dahl KD, et al. Hypoxia affects mesoderm and enhances hemangioblast specification during early development. Development. 2004;131:4623–4634. - PubMed

