Treatment of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 20135728
- PMCID: PMC2817068
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i6.770
Treatment of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy of antiviral or corticosteroid treatment on hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis (HBV-GN).
Methods: Six and five trials were used respectively to evaluate the efficacy of either antiviral or corticosteroid treatment on HBV-GN. Pediatric patients were pooled separately to assess their response to the above treatment modalities. The primary and secondary outcomes were remission of proteinuria and clearance of Hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg), respectively. A fixed or random effect model was established to collect the data.
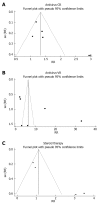
Results: The remission rate of proteinuria (RR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.08-2.65) and the clearance rate of HBeAg (RR = 6.44, 95% CI: 3.11-13.35) were significantly higher in antiviral treatment group than in control group. The proteinuria remission was significantly associated with HBeAg clearance (P = 0.002). However, the difference in proteinuria remission rate was not statistically significant between corticosteroid treatment group and control group (RR = 1.45, 95% CI: 0.68-3.11). Antiviral therapy could significantly promote the HBeAg clearance in pediatric patients, but neither antiviral nor corticosteroid therapy could significantly decrease proteinuria in pediatric patients compared to controls.
Conclusion: Antiviral but not corticosteroid treatment can decrease proteinuria and promote HBeAg clearance in HBV-GN patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of combined therapy for adult hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Feb 28;18(8):821-32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i8.821. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22371643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of nucleotide/nucleoside analog monotherapy for hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis.Clin Nephrol. 2016 Jan;85(1):21-9. doi: 10.5414/CN108648. Clin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26636326 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of anti-viral therapy for Hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 15;15(1):e0227532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227532. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31940324 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of hepatitis B virus associated glomerulonephritis with recombinant human alpha interferon.Am J Nephrol. 1997;17(2):112-7. doi: 10.1159/000169083. Am J Nephrol. 1997. PMID: 9096440
-
Interferon therapy for HCV-associated glomerulonephritis: meta-analysis of controlled trials.Int J Artif Organs. 2007 Mar;30(3):212-9. doi: 10.1177/039139880703000306. Int J Artif Organs. 2007. PMID: 17417760 Review.
Cited by
-
Sudden deterioration of renal function in a patient with nephrotic syndrome and a very high hepatitis B viral DNA load.J Renal Inj Prev. 2012 Jan 1;1(1):39-41. doi: 10.12861/jrip.2012.14. eCollection 2012. J Renal Inj Prev. 2012. PMID: 25340103 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of Hepatitis C Virus and Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the Setting of Kidney Disease.Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023 Jul;30(4):343-355. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2023.04.003. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023. PMID: 37657881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of telbivudine antiviral treatment in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: A 104-week pilot study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(31):e11716. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011716. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30075577 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis of Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Membranous Nephropathy.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 6;11(9):e0160437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160437. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27598699 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable outcome in PLA2R positive HBV-associated membranous nephropathy.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Jul 11;23(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02871-y. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35818032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhimma R, Coovadia HM, Adhikari M, Connolly CA. The impact of the hepatitis B virus vaccine on the incidence of hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157:1025–1030. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Sun L, Zhou LJ, Fang LJ, Sheng FY, Guo YQ. The effect of hepatitis B vaccination on the incidence of childhood HBV-associated nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2003;18:1216–1219. - PubMed
-
- Walters S, Levin M. Infectious diseases and the kidney. In: Barratt TM, Avner ED, Harmon WE, editors. Pediatric Nephrology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999. pp. 1088–1090.
-
- Lai KN, Lai FM, Chan KW, Chow CB, Tong KL, Vallance-Owen J. The clinico-pathologic features of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis. Q J Med. 1987;63:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert RD, Wiggelinkhuizen J. The clinical course of hepatitis B virus-associated nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994;8:11–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

