DNA carrier testing and newborn screening for maple syrup urine disease in Old Order Mennonite communities
- PMID: 20136525
- PMCID: PMC5586154
- DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2009.0107
DNA carrier testing and newborn screening for maple syrup urine disease in Old Order Mennonite communities
Abstract
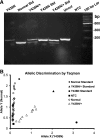
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by mutations in the branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Worldwide incidence of MSUD is 1:225,000 live births. However, within Old Order Mennonite communities, the incidence is 1:150 live births and results from a common tyrosine to asparagine substitution (Y438N) in the E1alpha subunit of branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. We developed a new DNA diagnostic assay utilizing TaqMan technology and compared its efficacy, sensitivity, and duration with an existing polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay. Carrier testing was performed by both TaqMan technology and PCR-RFLP on DNA isolated from buccal swabs of 160 individuals as well as from buccal swabs and blood spots of nine at-risk newborns; assay time, sensitivity, and reliability were also evaluated. The TaqMan assay, like the PCR-RFLP assay, accurately determined Y438N E1alpha allele status. However, the TaqMan assay appeared (1) more sensitive than the PCR-RFLP assay, requiring 10-fold less DNA (10 ng) to reliably determine genotype status and (2) faster, reducing the assay time required for diagnosis from approximately 12 to 5 h. TaqMan technology allowed more rapid DNA diagnoses of MSUD in the neonate, thereby reducing the likelihood of neurological impairment while enhancing health and prognosis for affected infants.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carrier detection and rapid newborn diagnostic test for the common Y393N maple syrup urine disease allele by PCR-RFLP: culturally permissible testing in the Mennonite community.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2001 Jun;24(3):393-403. doi: 10.1023/a:1010517005001. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2001. PMID: 11486905
-
Evidence of common ancestry for the maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) Y438N allele in non-Mennonite MSUD patients.Mol Genet Metab. 2002 Jan;75(1):79-90. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2001.3264. Mol Genet Metab. 2002. PMID: 11825067
-
Occurrence of a Tyr393----Asn (Y393N) mutation in the E1 alpha gene of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex in maple syrup urine disease patients from a Mennonite population.Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):429-34. Am J Hum Genet. 1991. PMID: 1867199 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress of research on Maple syrup disease].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Jul 10;36(7):737-741. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2019.07.021. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31302925 Review. Chinese.
-
Maple syrup urine disease: it has come a long way.J Pediatr. 1998 Mar;132(3 Pt 2):S17-23. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70523-2. J Pediatr. 1998. PMID: 9546032 Review.
Cited by
-
A founder AGL mutation causing glycogen storage disease type IIIa in Inuit identified through whole-exome sequencing: a case series.CMAJ. 2015 Feb 3;187(2):E68-E73. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.140840. Epub 2015 Jan 19. CMAJ. 2015. PMID: 25602008 Free PMC article.
-
High proportion of transient neonatal zinc deficiency causing alleles in the general population.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):828-840. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13982. Epub 2018 Nov 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30450693 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of gene mutations in six Chinese patients with maple syrup urine disease.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 24;14:1132364. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1132364. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36911408 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of acute metabolic decompensation in children with maple syrup urine disease at the emergency department.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Jul;179(7):1107-1114. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03602-x. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32048023
-
[Disease spectrum and pathogenic genes of inherited metabolic disorder in Gansu Province of China].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jan 15;26(1):67-71. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2308094. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38269462 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Chuang DT. Maple syrup urine disease: it has come a long way. J Pediatr. 1998;132:S17–S23. - PubMed
-
- Danner DJ. Doering CB. Human mutations affecting branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase. Front Biosci. 1998;3:d517–d524. - PubMed
-
- Danner DJ. Elsas LJ. Valle D. Disorders of branched chain amino acid and keto acid metabolism. In: Scriver CR, editor; Beaudet AL, editor; Sly WS, editor; The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. I. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1989. pp. 671–692.
-
- Livak KJ. Allelic discrimination using fluorogenic probes and the 5′ nuclease assay. Genet Anal. 1999;14:143–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

