Somatotopic organization of lumbar muscle-innervating neurons in the ventral horn of the rat spinal cord
- PMID: 20136668
- PMCID: PMC2849526
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01203.x
Somatotopic organization of lumbar muscle-innervating neurons in the ventral horn of the rat spinal cord
Abstract
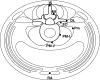
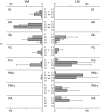
The ventral horn of the rat spinal cord was investigated with respect to the somatotopic organization of the motor neurons that innervate the lumbar muscles. Neurotracer 1,1'-dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) was applied to specific sites in lumbar muscles. Spinal cord segments at L1 through L4 levels were cut into 40-mum serial transverse sections. Labeled neurons were located in the ventromedial nucleus (VM) and lateromedial nucleus (LM) nuclei of Rexed's lamina IX. Motor neurons innervating the m. interspinales lumborum and m. multifidus were without exception present in the VM, whereas all motor neurons innervating the m. rectus abdominis were present in the LM. Forty percent of motor neurons innervating the m. quadratus lumborum were present in the VM and the other 60% were in the LM. Although most of the motor neurons innervating the m. psoas major were present in the LM, a few labeled neurons existed in the VM. These results suggest that the border zone demarcating the areas of innervation of the dorsal and ventral rami of spinal nerves crosses the m. quadratus lumborum.
Figures




References
-
- Bogduk N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1983;8:286–293. - PubMed
-
- Bogduk N. Nerves of the lumbar spine. In: Bogduk N, editor. Clinical Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine and Sacrum. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1997. p. 143.
-
- Brown PB, Fuchs JL. Somatotopic representation of hindlimb skin in cat dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 1975;38:1–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

