Vasodilator therapy with hydralazine induces angiotensin AT receptor-mediated cardiomyocyte growth in mice lacking guanylyl cyclase-A
- PMID: 20136844
- PMCID: PMC2839271
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00619.x
Vasodilator therapy with hydralazine induces angiotensin AT receptor-mediated cardiomyocyte growth in mice lacking guanylyl cyclase-A
Abstract
Background and purpose: Recent clinical guidelines advocate the use of the isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine combination in treatment for heart failure. However, clinical and laboratory evidence suggest that some vasodilators may induce cardiac hypertrophy under uncertain conditions. This study investigated the effects and underlying mechanism of action of the vasodilator hydralazine on cardiac growth.
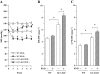
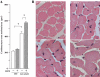
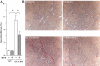
Experimental approach: Wild-type mice and animals deficient in guanylyl cyclase-A (GCA) and/or angiotensin receptors (AT(1) and AT(2) subtypes) were treated with hydralazine ( approximately 24 mg.kg(-1).day(-1) in drinking water) for 5 weeks. Cardiac mass and/or cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area, fibrosis (van Giessen-staining) and cardiac gene expression (real-time RT-PCR) were measured.
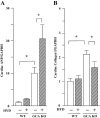
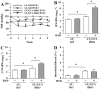
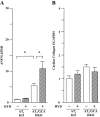
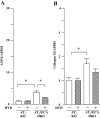
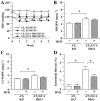
Key results: Hydralazine lowered blood pressure in mice of all genotypes. However, this treatment increased the heart and left ventricular to body weight ratios, as well as cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area, and cardiac expression of atrial natriuretic peptide mRNA in mice lacking GCA. Hydralazine did not affect cardiac hypertrophy in wild-type mice and mice lacking either AT(1) or AT(2) receptors alone. However, the pro-hypertrophic effect of hydralazine was prevented in mice lacking both GCA and AT(2), but not GCA and AT(1) receptors. However, hydralazine did decrease cardiac collagen deposition and collagen I mRNA (signs of cardiac fibrosis) in mice that were deficient in GCA, or both GCA and AT(2) receptors.
Conclusions and implications: The vasodilator hydralazine induced AT(2) receptor-mediated cardiomyocyte growth under conditions of GCA deficiency. However, attenuation of cardiac fibrosis by hydralazine could be beneficial in the management of cardiac diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guanylyl cyclase-A inhibits angiotensin II type 2 receptor-mediated pro-hypertrophic signaling in the heart.Endocrinology. 2009 Aug;150(8):3759-65. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1353. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19372206
-
Role of natriuretic peptide receptor guanylyl cyclase-A in myocardial infarction evaluated using genetically engineered mice.Hypertension. 2005 Aug;46(2):441-7. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000173420.31354.ef. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 15998711
-
Genetic disruption of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A upregulates ACE and AT1 receptor gene expression and signaling: role in cardiac hypertrophy.Physiol Genomics. 2007 Oct 22;31(2):193-202. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00079.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Physiol Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17566078
-
[Cardiovascular significance of the natriuretic peptide receptor, guanylyl cyclase-A, from studies using genetically engineered mice].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Sep;62 Suppl 9:38-42. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15506333 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Role of the renin-angiotensin system in cardiac hypertrophy.Am J Cardiol. 1999 Jun 17;83(12A):53H-57H. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00259-3. Am J Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 10750588 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced density gradient as a novel approach for estimating QSAR descriptors, and its application to 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives with potential antihypertensive effects.J Mol Model. 2016 Dec;22(12):296. doi: 10.1007/s00894-016-3159-x. Epub 2016 Nov 26. J Mol Model. 2016. PMID: 27889884
-
Dose-Dependent Effects of Long-Term Administration of Hydrogen Sulfide on Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Male Wistar Rats: Modulation of RKIP, NF-κB, and Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1415. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041415. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer JA, Fung HL. Concurrent hydralazine administration prevents nitroglycerin-induced hemodynamic tolerance in experimental heart failure. Circulation. 1991;84:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar RS, Rapaka SSR, Liu TZ, Wolfe SM. Hydralazine-induced disturbances in collagen biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972;271:125–132. - PubMed
-
- D'Amore A, Black MJ, Thomas WG. The angiotensin II type 2 receptor causes constitutive growth of cardiomyocytes and does not antagonize angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated hypertrophy. Hypertension. 2005;46:1347–1354. - PubMed
-
- Fenje P, Leenen FH. Effects of minoxidil on blood pressure and cardiac hypertrophy in two-kidney, one-clip hypertensive rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985;63:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Gerber JG, Nies AS. Ahtihypertensive agents and the drug therapy of hypertension. In: Gilman AG, Rall TW, Nies AS, Taylor P, editors. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. New York: Pergamon Press; 1990. pp. 784–813.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

