Emesis in dogs: a review
- PMID: 20137004
- PMCID: PMC7167204
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-5827.2009.00820.x
Emesis in dogs: a review
Abstract
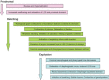
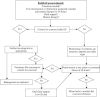
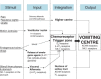
Emesis is a common presenting sign in small animal practice. It requires a rational approach to management that is based upon a sound understanding of pathophysiology combined with logical decision making. This review, which assesses the weight of available evidence, outlines the physiology of the vomiting reflex, causes of emesis, the consequences of emesis and the approach to clinical management of the vomiting dog. The applicability of diagnostic testing modalities and the merit of traditional approaches to management, such as dietary changes, are discussed. The role and usefulness of both traditional and novel anti-emetic drugs is examined, including in specific circumstances such as following cytotoxic drug treatment. The review also examines areas in which common clinical practice is not necessarily supported by objective evidence and, as such, highlights questions worthy of further clinical research.
Figures
References
-
- Abe, T. , Kieser, T. M. , Tomita, T. & Easton, P. A. (1994) Respiratory muscle function during emesis in awake canines. Journal of Applied Physiology 76, 2552–2560 - PubMed
-
- Abe, T. , Kusuhara, N. , Katagiri, H. , Tomita, T. & Easton, P. A. (1993) Differential function of the costal and crural diaphragm during emesis in canines. Respiratory Physiology 91, 183–193 - PubMed
-
- Abood, S. K. & Buffington, C. A. (1992) Enteral feeding of dogs and cats: 51 cases (1989‐1991). Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 201, 619–622 - PubMed
-
- Aroch, I. , Nyska, A. , Gal, R. & Bark, H. (1997) Functional intestinal hypomotility in association with neuronal damage in a dog. Journal of Small Animal Practice 38, 119–123 - PubMed
-
- Bellenger, C. R. , Maddison, J. E. , MacPherson, G. C. & Ilkiw, J. E. (1990) Chronic hypertrophic pyloric gastropathy in 14 dogs. Australian Veterinary Journal 67, 317–320 - PubMed
APPENDIX 1
References to tables
-
- Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine (2001) http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=1047 Accessed March 17th 2009.
-
- Hayden, D. W. & Fleischman, R. W. (1977) Scirrhous eosinophilic gastritis in dogs with gastric arteritis. Veterinary Quarterly 14, 441–448 - PubMed
-
- Tyszko, C. , Bright, J. M. & Swist, S. L. (2007) Recurrent supraventricular arrhythmias in a dog with atrial myocarditis and gastritis. Journal of Small Animal Practice 48, 335–338 - PubMed
-
- van der Gaag, I. , Happe, R. P. & Wolvekamp, W. T. (1976) A boxer dog with chronic hypertrophic gastritis resembling Menetrier’s disease in man. Veterinary Quarterly 13, 172–185 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

