FcRgamma activation regulates inflammation-associated squamous carcinogenesis
- PMID: 20138013
- PMCID: PMC3082507
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.019
FcRgamma activation regulates inflammation-associated squamous carcinogenesis
Abstract
Chronically activated leukocytes recruited to premalignant tissues functionally contribute to cancer development; however, mechanisms underlying pro- versus anti-tumor programming of neoplastic tissues by immune cells remain obscure. Using the K14-HPV16 mouse model of squamous carcinogenesis, we report that B cells and humoral immunity foster cancer development by activating Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaRs) on resident and recruited myeloid cells. Stromal accumulation of autoantibodies in premalignant skin, through their interaction with activating FcgammaRs, regulate recruitment, composition, and bioeffector functions of leukocytes in neoplastic tissue, which in turn promote neoplastic progression and subsequent carcinoma development. These findings support a model in which B cells, humoral immunity, and activating FcgammaRs are required for establishing chronic inflammatory programs that promote de novo carcinogenesis.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
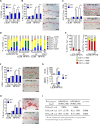
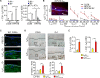
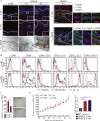

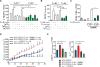
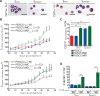
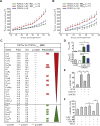
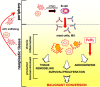
Comment in
-
La mala educación of tumor-associated macrophages: Diverse pathways and new players.Cancer Cell. 2010 Feb 17;17(2):111-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.01.019. Cancer Cell. 2010. PMID: 20159603
References
-
- Arbeit JM, Olson DC, Hanahan D. Upregulation of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors during multi-stage epidermal carcinogenesis in K14-HPV16 transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1996;13:1847–1857. - PubMed
-
- Baumann U, Chouchakova N, Gewecke B, Kohl J, Carroll MC, Schmidt RE, Gessner JE. Distinct tissue site-specific requirements of mast cells and complement components C3/C5a receptor in IgG immune complex-induced injury of skin and lung. J. Immunol. 2001;167:1022–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA130980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA72006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA09043/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009043/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- TGT06S01/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- R01 CA140943/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA130980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA108462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA108462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA072006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA13256/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA098075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

