Loss of synaptotagmin IV results in a reduction in synaptic vesicles and a distortion of the Golgi structure in cultured hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 20138128
- PMCID: PMC3102522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.056
Loss of synaptotagmin IV results in a reduction in synaptic vesicles and a distortion of the Golgi structure in cultured hippocampal neurons
Abstract
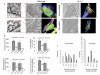
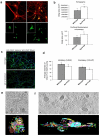
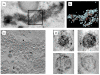
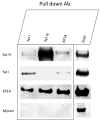
Fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane is mediated by the SNARE (soluble NSF attachment receptor) proteins and is regulated by synaptotagmin (syt). There are at least 17 syt isoforms that have the potential to act as modulators of membrane fusion events. Synaptotagmin IV (syt IV) is particularly interesting; it is an immediate early gene that is regulated by seizures and certain classes of drugs, and, in humans, syt IV maps to a region of chromosome 18 associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disease. Syt IV has recently been found to localize to dense core vesicles in hippocampal neurons, where it regulates neurotrophin release. Here we have examined the ultrastructure of cultured hippocampal neurons from wild-type and syt IV -/- mice using electron tomography. Perhaps surprisingly, we observed a potential synaptic vesicle transport defect in syt IV -/- neurons, with the accumulation of large numbers of small clear vesicles (putative axonal transport vesicles) near the trans-Golgi network. We also found an interaction between syt IV and KIF1A, a kinesin known to be involved in vesicle trafficking to the synapse. Finally, we found that syt IV -/- synapses exhibited reduced numbers of synaptic vesicles and a twofold reduction in the proportion of docked vesicles compared to wild-type. The proportion of docked vesicles in syt IV -/- boutons was further reduced, 5-fold, following depolarization.
Copyright 2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bai J, Wang CT, Richards DA, Jackson MB, Chapman ER. Fusion pore dynamics are regulated by synaptotagmin*t-SNARE interactions. Neuron. 2004;41:929–942. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977;126:397–342. - PubMed
-
- Berton F, Cornet V, Iborra C, Garrido J, Dargent B, Fukuda M, Seagar M, Marqueze B. Synaptotagmin I and IV define distinct populations of neuronal transport vesicles. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:1294–1302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

