Intrinsic fluoroquinolone resistance in Orientia tsutsugamushi
- PMID: 20138477
- PMCID: PMC7610924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.11.019
Intrinsic fluoroquinolone resistance in Orientia tsutsugamushi
Abstract
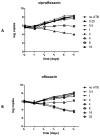
Scrub typhus is a public health concern for a population of over a billion humans, with an estimated incidence of one million cases/year in endemic areas. Although doxycycline remains the standard therapy, fluoroquinolones have been used successfully in a few patients. However, there is also clinical evidence that fluoroquinolones are ineffective in the treatment of scrub typhus. To clarify this matter, we determined the in vitro susceptibility of Orientia tsutsugamushi strain Kato to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin and sequenced the quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) of the gyrA gene, the target of fluoroquinolones, of 18 fresh isolates from the Lao PDR. Orientia tsutsugamushi strain Kato was resistant to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin in vitro (minimum inhibitory concentration=8 microg/mL). All sequences obtained, including those from the two available genomes of O. tsutsugamushi (strains Boryong and Ikeda), had a Ser83Leu mutation in their QRDR domain that is known to be associated with fluoroquinolone resistance. These findings re-emphasise the usefulness of in silico analysis for the prediction of antibiotic resistance and suggest that fluoroquinolones should not be used in the treatment of scrub typhus.
(c) 2009 Elsevier B.V. and the International Society of Chemotherapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Fournier PE, Siritantikorn S, Rolain JM, Suputtamongkol Y, Hoontrakul S, Charoenwat S, et al. Detection of new genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi infecting humans in Thailand. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14:168–73. - PubMed
-
- Cracco C, Delafosse C, Baril L, Lefort Y, Morelot C, Derenne JP, et al. Multiple organ failure complicating probable scrub typhus. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:191–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

