Polycystic liver diseases
- PMID: 20138815
- PMCID: PMC2894157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2010.01.006
Polycystic liver diseases
Abstract
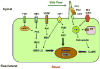
Polycystic liver diseases (PCLDs) are genetic disorders with heterogeneous etiologies and a range of phenotypic presentations. PCLD exhibits both autosomal or recessive dominant pattern of inheritance and is characterized by the progressive development of multiple cysts, isolated or associated with polycystic kidney disease, that appear more extensive in women. Cholangiocytes have primary cilia, functionally important organelles (act as mechanosensors) that are involved in both normal developmental and pathological processes. The absence of polycystin-1, 2, and fibrocystin/polyductin, normally localized to primary cilia, represent a potential mechanism leading to cyst formation, associated with increased cell proliferation and apoptosis, enhanced fluid secretion, abnormal cell-matrix interactions, and alterations in cell polarity. Proliferative and secretive activities of cystic epithelium can be regulated by estrogens either directly or by synergizing growth factors including nerve growth factor, IGF1, FSH and VEGF. The abnormalities of primary cilia and the sensitivity to proliferative effects of estrogens and different growth factors in PCLD cystic epithelium provide the morpho-functional basis for future treatment targets, based on the possible modulation of the formation and progression of hepatic cysts.
Copyright (c) 2010 Editrice Gastroenterologica Italiana S.r.l. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Everson GT, Helmke SM, Doctor B. Advances in management of polycystic liver disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2:563–76. - PubMed
-
- Masyuk T, LaRusso N. Polycystic liver disease: new insights into disease pathogenesis. Hepatology. 2006;43:906–8. - PubMed
-
- Everson GT, Taylor MR, Doctor RB. Polycystic disease of the liver. Hepatology. 2004;40:774–82. - PubMed
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

