A molecular mechanism for proton-dependent gating in KcsA
- PMID: 20138880
- PMCID: PMC2858269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.003
A molecular mechanism for proton-dependent gating in KcsA
Abstract
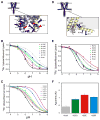
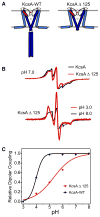
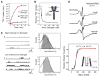
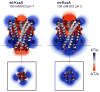
Activation gating in KcsA is elicited by changes in intracellular proton concentration. Thompson et al. identified a charge cluster around the inner gate that plays a key role in defining proton activation in KcsA. Here, through functional and spectroscopic approaches, we confirmed the role of this charge cluster and now provide a mechanism of pH-dependent gating. Channel opening is driven by a set of electrostatic interactions that include R117, E120 and E118 at the bottom of TM2 and H25 at the end of TM1. We propose that electrostatic compensation in this charge cluster stabilizes the closed conformation at neutral pH and that its disruption at low pH facilitates the transition to the open conformation by means of helix-helix repulsion.
Copyright 2010 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer; Sunderland, MA: 1992.
-
- Yellen G. The moving parts of voltage-gated ion channels. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. 1998;31:239–95. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong CM. Sci STKE 2003. 2003. Voltage-gated K channels; p. re10. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K, Takahashi H, Kawano S, Shimada I. Identification and characterization of the slowly exchanging pH-dependent conformational rearrangement in KcsA. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15179–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

