Three dimensional echo-planar imaging at 7 Tesla
- PMID: 20139009
- PMCID: PMC2853246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.108
Three dimensional echo-planar imaging at 7 Tesla
Abstract
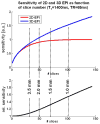
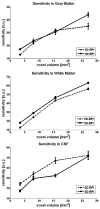
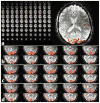
Functional MRI (fMRI) most commonly employs 2D echo-planar imaging (EPI). The advantages for fMRI brought about by the increasingly popular ultra-high field strengths are best exploited in high-resolution acquisitions, but here 2D EPI becomes impractical for several reasons, including the very long volume acquisitions times. In this study at 7 T, a 3D EPI sequence with full parallel and partial Fourier imaging capability along both phase encoding axes was implemented and used to evaluate the sensitivity of 3D and corresponding 2D EPI acquisitions at four different spatial resolutions ranging from small to typical voxel sizes (1.5-3.0 mm isotropic). Whole-brain resting state measurements (N=4) revealed a better, or at least comparable sensitivity of the 3D method for gray and white matter. The larger vulnerability of 3D to physiological effects was outweighed by the much shorter volume TR, which moreover allows whole-brain coverage at high resolution within fully acceptable limits for event-related fMRI: TR was only 3.07 s for 1.5 mm, 1.88 s for 2.0 mm, 1.38 s for 2.5 mm and 1.07 s for 3.0 mm isotropic resolution. In order to investigate the ability to detect and spatially resolve BOLD activation in the visual cortex, functional 3D EPI experiments (N=8) were performed at 1 mm isotropic resolution with parallel imaging acceleration of 3x3, resulting in a TR of only 3.2 s for whole-brain coverage. From our results, and several other practical advantages of 3D over 2D EPI found in the present study, we conclude that 3D EPI provides a useful alternative for whole-brain fMRI at 7 T, not only when high-resolution data are required.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- de Zwart JA, van Gelderen P, Golay X, Ikonomidou VN, Duyn JH. Accelerated parallel imaging for functional imaging of the human brain. NMR Biomed. 2006;19:342–351. - PubMed
-
- de Zwart JA, van Gelderen P, Kellman P, Duyn JH. Application of sensitivity-encoded echo-planar imaging for blood oxygen level-dependent functional brain imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2002;48:1011–1020. - PubMed
-
- Golay X, Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Crelier GR, Folkers PJ, Kollias SS, Boesiger P. PRESTO-SENSE: an ultrafast whole-brain fMRI technique. Magn Reson Med. 2000;43:779–786. - PubMed
-
- Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA) Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:1202–1210. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Glover G. Increasing the sensitivity to BOLD contrast in high resolution fMRI studies by using 3D spiral technique. Proceedings of the 15th Annual Meeting of ISMRM; Berlin. 1945.2007a.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

