Cul8/Rtt101 forms a variety of protein complexes that regulate DNA damage response and transcriptional silencing
- PMID: 20139071
- PMCID: PMC2843234
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082107
Cul8/Rtt101 forms a variety of protein complexes that regulate DNA damage response and transcriptional silencing
Abstract
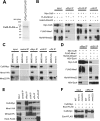
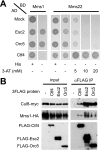
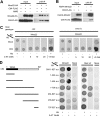
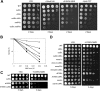
The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has three cullin proteins, which act as platforms for Cullin-based E3 ubiquitin ligases. Genetic evidence indicates that Cul8, together with Mms1, Mms22, and Esc4, is involved in the repair of DNA damage that can occur during DNA replication. Cul8 is thought to form a complex with these proteins, but the composition and the function of Cul8-based E3 ubiquitin ligases remain largely uncharacterized. Herein, we report a comprehensive biochemical analysis of Cul8 complexes. Cul8 was found to form a Cul8-Mms1-Mms22-Esc4 complex under physiological conditions, with Mms1 bridging Cul8 and Mms22 and Mms22 bridging Mms1 and Esc4. Domain analysis demonstrated that the N-terminal region of Mms1 and the C-terminal region of Mms22 are required for the Mms1-Mms22 interaction, whereas the N-terminal region of Mms22 is required for the Mms22-Esc4 interaction. We also found other Cul8-Mms1-binding proteins Ctf4, Esc2, and Orc5 using yeast two-hybrid screening. Esc4 and Ctf4 bound to Mms22 directly and bound to Cul8-Mms1 in the presence of Mms22, whereas Esc2 and Orc5 interacted with both Cul8 and Mms1, independently. We found that Cul8, Mms1, and Mms22 participated in the regulation of transcriptional silencing of yeast telomeres. These results suggest that Cul8-Mms1, as part of various protein complexes, is involved in the regulation of chromatin metabolism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mms1 and Mms22 stabilize the replisome during replication stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 1;22(13):2396-408. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-10-0848. Epub 2011 May 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21593207 Free PMC article.
-
Rtt101 and Mms1 in budding yeast form a CUL4(DDB1)-like ubiquitin ligase that promotes replication through damaged DNA.EMBO Rep. 2008 Oct;9(10):1034-40. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.155. Epub 2008 Aug 15. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18704118 Free PMC article.
-
The Replisome-Coupled E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Rtt101Mms22 Counteracts Mrc1 Function to Tolerate Genotoxic Stress.PLoS Genet. 2016 Feb 5;12(2):e1005843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005843. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26849847 Free PMC article.
-
Budding yeast Mms22 and Mms1 regulate homologous recombination induced by replisome blockage.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 May 3;7(5):811-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.01.007. Epub 2008 Mar 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18321796
-
ISWI complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 15;1677(1-3):100-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2003.10.014. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15020051 Review.
Cited by
-
The MMS22L-TONSL complex mediates recovery from replication stress and homologous recombination.Mol Cell. 2010 Nov 24;40(4):619-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.024. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 21055983 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochromatin formation via recruitment of DNA repair proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Apr 1;26(7):1395-410. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1413. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25631822 Free PMC article.
-
MMS22L-TONSL functions in sister chromatid cohesion in a pathway parallel to DSCC1-RFC.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Dec 8;6(2):e202201596. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201596. Print 2023 Feb. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36622344 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised maximum-likelihood weighting of composite protein networks for complex prediction.BMC Syst Biol. 2012;6 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S13. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-S2-S13. Epub 2012 Dec 12. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 23281936 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-BRCT scaffolds use distinct strategies to support genome maintenance.Cell Cycle. 2016 Oct;15(19):2561-2570. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1218102. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27580271 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

