Metabolomic changes accompanying transformation and acquisition of metastatic potential in a syngeneic mouse mammary tumor model
- PMID: 20139083
- PMCID: PMC2843179
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C110.104448
Metabolomic changes accompanying transformation and acquisition of metastatic potential in a syngeneic mouse mammary tumor model
Abstract
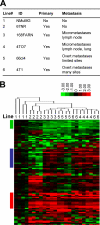
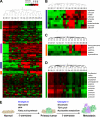
Breast cancer is the most common cancer type for women in the western world. Despite decades of research, the molecular processes associated with breast cancer progression are still inadequately defined. Here, we focus on the systematic alteration of metabolism by using the state of the art metabolomic profiling techniques to investigate the changes of 157 metabolites during the progression of normal mouse mammary epithelial cells to an isogenic series of mammary tumor cell lines with increasing metastatic potentials. Our results suggest a two-step metabolic progression hypothesis during the acquisition of tumorigenic and metastatic abilities. Metabolite changes accompanying tumor progression are identified in the intracellular and secreted forms in several pathways, including glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, the pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid and nucleotide biosynthesis, and the GSH-dependent antioxidative pathway. These results suggest possible biomarkers of breast cancer progression as well as opportunities of interrupting tumor progression through the targeting of metabolic pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Murray T., Thun M. J. (2008) CA Cancer J. Clin. 58, 71–96 - PubMed
-
- Lu X., Kang Y. (2007) J Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 12, 153–162 - PubMed
-
- Kang Y., Siegel P. M., Shu W., Drobnjak M., Kakonen S. M., Cordón-Cardo C., Guise T. A., Massagué J. (2003) Cancer Cell 3, 537–549 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

