The Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor AKAP13 (BRX) is essential for cardiac development in mice
- PMID: 20139090
- PMCID: PMC2852973
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.106856
The Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor AKAP13 (BRX) is essential for cardiac development in mice
Abstract
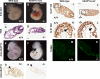
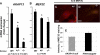
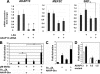
A fundamental biologic principle is that diverse biologic signals are channeled through shared signaling cascades to regulate development. Large scaffold proteins that bind multiple proteins are capable of coordinating shared signaling pathways to provide specificity to activation of key developmental genes. Although much is known about transcription factors and target genes that regulate cardiomyocyte differentiation, less is known about scaffold proteins that couple signals at the cell surface to differentiation factors in developing heart cells. Here we show that AKAP13 (also known as Brx-1, AKAP-Lbc, and proto-Lbc), a unique protein kinase A-anchoring protein (AKAP) guanine nucleotide exchange region belonging to the Dbl family of oncogenes, is essential for cardiac development. Cardiomyocytes of Akap13-null mice had deficient sarcomere formation, and developing hearts were thin-walled and mice died at embryonic day 10.5-11.0. Disruption of Akap13 was accompanied by reduced expression of Mef2C. Consistent with a role of AKAP13 upstream of MEF2C, Akap13 siRNA led to a reduction in Mef2C mRNA, and overexpression of AKAP13 augmented MEF2C-dependent reporter activity. The results suggest that AKAP13 coordinates Galpha(12) and Rho signaling to an essential transcription program in developing cardiomyocytes.
Figures




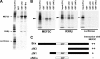
Similar articles
-
Mice Deficient in AKAP13 (BRX) Are Osteoporotic and Have Impaired Osteogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Oct;30(10):1887-95. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2534. Epub 2015 May 10. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25892096 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP13 Rho-GEF and PKD-binding domain deficient mice develop normally but have an abnormal response to β-adrenergic-induced cardiac hypertrophy.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 26;8(4):e62705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062705. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Dec 12;18(12):e0296004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296004. PMID: 23658642 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Analysis Shows AKAP13-Mediated PKD1 Signaling Regulates the Transcriptional Response to Cardiac Hypertrophy.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0132474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132474. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26192751 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP-Lbc: a molecular scaffold for the integration of cyclic AMP and Rho transduction pathways.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):603-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16460837 Review.
-
Regulation and physiological functions of G12/13-mediated signaling pathways.Neurosignals. 2009;17(1):55-70. doi: 10.1159/000186690. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Neurosignals. 2009. PMID: 19212140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mice Deficient in AKAP13 (BRX) Are Osteoporotic and Have Impaired Osteogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Oct;30(10):1887-95. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2534. Epub 2015 May 10. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25892096 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the activation of the RhoA GTPase by the lymphoid blast crisis (Lbc) oncoprotein.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 22;289(34):23992-4004. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.561787. Epub 2014 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24993829 Free PMC article.
-
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors: regulators of Rho GTPase activity in development and disease.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 31;33(31):4021-35. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.362. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24037532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKAP13 Rho-GEF and PKD-binding domain deficient mice develop normally but have an abnormal response to β-adrenergic-induced cardiac hypertrophy.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 26;8(4):e62705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062705. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Dec 12;18(12):e0296004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296004. PMID: 23658642 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The C-terminus of the long AKAP13 isoform (AKAP-Lbc) is critical for development of compensatory cardiac hypertrophy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jan;66:27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Oct 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24161911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubino D., Driggers P., Arbit D., Kemp L., Miller B., Coso O., Pagliai K., Gray K., Gutkind S., Segars J. (1998) Oncogene 16, 2513–2526 - PubMed
-
- Miller B. T., Rubino D. M., Driggers P. H., Haddad B., Cisar M., Gray K., Segars J. H. (2000) Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 182, 286–295 - PubMed
-
- Diviani D., Soderling J., Scott J. D. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 44247–44257 - PubMed
-
- Toksoz D., Williams D. A. (1994) Oncogene 9, 621–628 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

