Analyses of the regulatory mechanism and physiological roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa OhrR, a transcription regulator and a sensor of organic hydroperoxides
- PMID: 20139188
- PMCID: PMC2849439
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01510-09
Analyses of the regulatory mechanism and physiological roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa OhrR, a transcription regulator and a sensor of organic hydroperoxides
Abstract
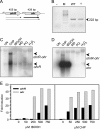
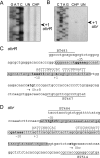
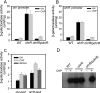
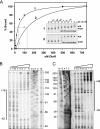
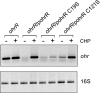
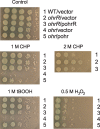
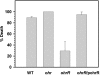
ohrR encodes an organic hydroperoxide sensor and a transcriptional repressor that regulates organic hydroperoxide-inducible expression of a thiol peroxidase gene, ohr, and itself. OhrR binds directly to the operators and represses transcription of these genes. Exposure to an organic hydroperoxide leads to oxidation of OhrR and to subsequent structural changes that result in the loss of the repressor's ability to bind to the operators that allow expression of the target genes. Differential induction of ohrR and ohr by tert-butyl hydroperoxide suggests that factors such as the repressor's dissociation constants for different operators and the chemical nature of the inducer contribute to OhrR-dependent organic hydroperoxide-inducible gene expression. ohrR and ohr mutants show increased and decreased resistance to organic hydroproxides, respectively, compared to a parental strain. Moreover, the ohrR mutant had a reduced-virulence phenotype in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Caenorhabditis elegans pathogenicity model.
Figures

References
-
- Alexeyev, M. F. 1999. The pKNOCK series of broad-host-range mobilizable suicide vectors for gene knockout and targeted DNA insertion into the chromosome of gram-negative bacteria. Biotechniques 26:824-826, 828. - PubMed
-
- Arun Kumar, C., and U. N. Das. 1999. Lipid peroxides, nitric oxide and essential fatty acids in patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 61:255-258. - PubMed
-
- Atichartpongkul, S., S. Loprasert, P. Vattanaviboon, W. Whangsuk, J. D. Helmann, and S. Mongkolsuk. 2001. Bacterial Ohr and OsmC paralogues define two protein families with distinct functions and patterns of expression. Microbiology 147:1775-1782. - PubMed
-
- Azenabor, A. A., and J. B. Mahony. 2000. Generation of reactive oxygen species and formation and membrane lipid peroxides in cells infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 4:46-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

