Myxococcus xanthus viability depends on groEL supplied by either of two genes, but the paralogs have different functions during heat shock, predation, and development
- PMID: 20139189
- PMCID: PMC2838048
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01458-09
Myxococcus xanthus viability depends on groEL supplied by either of two genes, but the paralogs have different functions during heat shock, predation, and development
Abstract
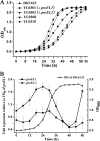
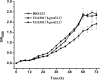
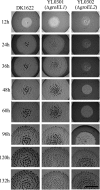
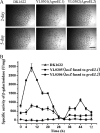
Myxococcus xanthus DK1622 contains two paralogous groEL gene loci that possess both different sequences and different organizations within the genome. Deletion of either one of these two genes alone does not affect cell viability. However, deletion of both groEL genes results in cell death unless a complemented groEL1 or groEL2 gene is present. The groEL1 gene was determined to be essential for cell survival under heat shock conditions; a strain with mutant groEL2 caused cells to be more sensitive than the wild-type strain to higher temperatures. Mutants with a single deletion of either groEL1 (MXAN_4895) or groEL2 (MXAN_4467) had a growth curve similar to that of the wild-type strain DK1622 in medium containing hydrolyzed proteins as the substrate. However, when cells were cultured on medium containing either Escherichia coli cells or casein as the substrate, deletion of groEL2, but not groEL1, led to a deficiency in cell predation and macromolecular feeding. Furthermore, groEL1 was found to play an indispensable role in the development and sporulation of cells, but deletion of groEL2 had no visible effects. Our results suggest that, although alternatively required for cell viability, the products of the two groEL genes have divergent functions in the multicellular social life cycle of M. xanthus DK1622.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms involved in the functional divergence of duplicated GroEL chaperonins in Myxococcus xanthus DK1622.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003306. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23437010 Free PMC article.
-
The groEL2 gene, but not groEL1, is required for biosynthesis of the secondary metabolite myxovirescin in Myxococcus xanthus DK1622.Microbiology (Reading). 2014 Mar;160(Pt 3):488-495. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.065862-0. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Microbiology (Reading). 2014. PMID: 24425771
-
Myxococcus xanthus DK1622 Coordinates Expressions of the Duplicate groEL and Single groES Genes for Synergistic Functions of GroELs and GroES.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 27;8:733. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00733. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28496436 Free PMC article.
-
Non-housekeeping, non-essential GroEL (chaperonin) has acquired novel structure and function beneficial under stress in cyanobacteria.Physiol Plant. 2017 Nov;161(3):296-310. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12595. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Physiol Plant. 2017. PMID: 28597961 Review.
-
The predatory life cycle of Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Jan;162(1):1-11. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000208. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 26518442 Review.
Cited by
-
The ecology of bacterial genes and the survival of the new.Int J Evol Biol. 2012;2012:394026. doi: 10.1155/2012/394026. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Int J Evol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22900231 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual-Functional Orphan Response Regulator Negatively Controls the Differential Transcription of Duplicate groELs and Plays a Global Regulatory Role in Myxococcus.mSystems. 2022 Apr 26;7(2):e0105621. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01056-21. Epub 2022 Mar 30. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35353010 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor mutations reveal an NtrC-like response regulator, NmpR, for modulation of Type-IV Pili-dependent motility in Myxococcus xanthus.PLoS Genet. 2018 Oct 22;14(10):e1007714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007714. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30346960 Free PMC article.
-
DnaK duplication and specialization in bacteria correlates with increased proteome complexity.mSystems. 2024 Apr 16;9(4):e0115423. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01154-23. Epub 2024 Mar 26. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38530057 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms involved in the functional divergence of duplicated GroEL chaperonins in Myxococcus xanthus DK1622.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003306. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23437010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bode, H. B., M. W. Ring, G. Schwar, R. M. Kroppenstedt, D. Kaiser, and R. Muller. 2006. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthase is involved in biosynthesis of isovaleryl-CoA in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus during fruiting body formation. J. Bacteriol. 188:6524-6528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dworkin, M., and D. Kaiser (ed.). 1993. Myxobacteria II. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

