Ste12 and Ste12-like proteins, fungal transcription factors regulating development and pathogenicity
- PMID: 20139240
- PMCID: PMC2863410
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00333-09
Ste12 and Ste12-like proteins, fungal transcription factors regulating development and pathogenicity
Abstract
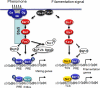
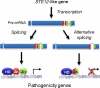
Ste12 and Ste12-like proteins are transcription factors found exclusively in the fungal kingdom. In the yeast model Saccharomyces cerevisiae, where the first member was identified, Ste12p was shown to regulate mating and invasive/pseudohyphal growth. In recent literature, there have been several reports of Ste12-like factors in multiple fungal systems, yeasts or filamentous fungi, with saprophytic or parasitic life-styles. In all these models, Ste12 and Ste12-like factors are involved in the regulation of fungal development and pathogenicity. In this review, we discuss the features, the regulation, and the role of Ste12 and Ste12-like factors by highlighting the similarities and dissimilarities that occur within this group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A ste12 allele having a differential effect on a versus alpha cells.Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Jan 6;246(1):80-90. doi: 10.1007/BF00290136. Mol Gen Genet. 1995. PMID: 7823915
-
Srb10/Cdk8 regulates yeast filamentous growth by phosphorylating the transcription factor Ste12.Nature. 2003 Jan 9;421(6919):187-90. doi: 10.1038/nature01243. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12520306
-
AFC1, a LAMMER kinase from Arabidopsis thaliana, activates STE12-dependent processes in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12105-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12105. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7991592 Free PMC article.
-
Coregulation of starch degradation and dimorphism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;32(5):405-35. doi: 10.3109/10409239709082675. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9383611 Review.
-
The Complex Genetic Basis and Multilayered Regulatory Control of Yeast Pseudohyphal Growth.Annu Rev Genet. 2021 Nov 23;55:1-21. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-071719-020249. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Annu Rev Genet. 2021. PMID: 34280314 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factor SsSte12 Was Involved in Mycelium Growth and Development in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 17;9:2476. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02476. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30386319 Free PMC article.
-
Extending the reach of homology by using successive computational filters to find yeast pheromone genes.Curr Biol. 2023 Oct 9;33(19):4098-4110.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.039. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37699395 Free PMC article.
-
α-Pheromone Precursor Protein Foc4-PP1 Is Essential for the Full Virulence of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense Tropical Race 4.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;9(3):365. doi: 10.3390/jof9030365. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983533 Free PMC article.
-
Prey sensing and response in a nematode-trapping fungus is governed by the MAPK pheromone response pathway.Genetics. 2021 Feb 9;217(2):iyaa008. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaa008. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33724405 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and morphological data support the existence of a sexual cycle in species of the genus Paracoccidioides.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 Mar;12(3):380-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.05052-11. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23125354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argimon S., Wishart J. A., Leng R., Macaskill S., Mavor A., Alexandris T., Nicholls S., Knight A. W., Enjalbert B., Walmsley R., Odds F. C., Gow N. A., Brown A. J. 2007. Developmental regulation of an adhesin gene during cellular morphogenesis in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 6:682–692 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao M. Z., Schwartz M. A., Cantin G. T., Yates J. R., III, Madhani H. D. 2004. Pheromone-dependent destruction of the Tec1 transcription factor is required for MAP kinase signaling specificity in yeast. Cell 119:991–1000 - PubMed
-
- Borneman A. R., Gianoulis T. A., Zhang Z. D., Yu H., Rozowsky J., Seringhaus M. R., Wang L. Y., Gerstein M., Snyder M. 2007. Divergence of transcription factor binding sites across related yeast species. Science 317:815–819 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

