IL-12 and IL-27 sequential gene therapy via intramuscular electroporation delivery for eliminating distal aggressive tumors
- PMID: 20139275
- PMCID: PMC2824785
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902371
IL-12 and IL-27 sequential gene therapy via intramuscular electroporation delivery for eliminating distal aggressive tumors
Abstract
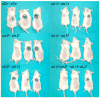
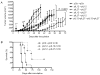
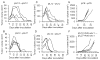
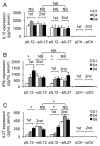
Eradication of residual malignancies and metastatic tumors via a systemic approach is the key for successfully treating cancer and increasing cancer patient survival. Systemic administration of IL-12 protein in an acute large dose is effective but toxic. Systemic administration of IL-12 gene by persistently expressing a low level of IL-12 protein may reduce the systemic toxicity but only eradicates IL-12-sensitive tumors. In this study, we discovered that sequential administration of IL-12- and IL-27-encoding DNA, referred to as sequential IL-12-->IL-27 (IL-12 administration followed by IL-27 administration 10 d after) gene therapy, not only eradicated IL-12-sensitive CT26 tumors from 100% of mice but also eradicated the highly malignant 4T1 tumors from 33% of treated mice in multiple independent experiments. This IL-12-->IL-27 sequential gene therapy is not only superior to IL-12-encoding plasmid DNA given a total of two times at a 10-d interval sequential gene therapy for eliminating tumors but also for inducing CTL activity, increasing T cell infiltration into tumors, and yielding a large number of tumor-specific IFN-gamma-positive CD8 T cells. Notably, depletion of either T or NK cells during the IL-27 treatment phase reverses tumor eradication, suggesting an NK cell requirement for this sequential gene therapy-mediated tumor eradication. Both reversal of the administration sequence and coadministration of IL-12 and IL-27 impaired tumor eradication in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice. This IL-12-->IL-27 sequential gene therapy, via sequential administration of IL-12- and IL-27-encoding plasmid DNA into tumor-bearing mice through i.m. electroporation, provides a simple but effective approach for eliminating inaccessible residual tumors.
Figures

References
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a cytokine produced by antigen-presenting cells with immunoregulatory functions in the generation of T-helper cells type 1 and cytotoxic lymphocytes. Blood. 1994;84:4008–4027. - PubMed
-
- Burke F. Cytokines (IFNs, TNF-alpha, IL-2 and IL-12) and animal models of cancer. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1999;5:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Golab J, Zagozdzon R. Antitumor effects of interleukin-12 in pre-clinical and early clinical studies (Review) Int J Mol Med. 1999;3:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Rakhmilevich AL, Janssen K, Turner J, Culp J, Yang NS. Cytokine gene therapy of cancer using gene gun technology: superior antitumor activity of interleukin-12. Hum Gene Ther. 1997;8:1303–1311. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe Y, Kuribayashi K, Miyatake S, Nishihara K, Nakayama E, Taniyama T, Sakata T. Exogenous expression of mouse interferon gamma cDNA in mouse neuroblastoma C1300 cells results in reduced tumorigenicity by augmented anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:9456–9460. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

