Role of extracellular DNA during biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 20139319
- PMCID: PMC2849236
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02361-09
Role of extracellular DNA during biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
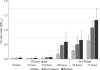
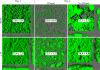
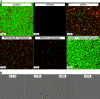
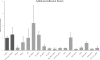
Listeria monocytogenes is a food-borne pathogen that is capable of living in harsh environments. It is believed to do this by forming biofilms, which are surface-associated multicellular structures encased in a self-produced matrix. In this paper we show that in L. monocytogenes extracellular DNA (eDNA) may be the only central component of the biofilm matrix and that it is necessary for both initial attachment and early biofilm formation for 41 L. monocytogenes strains that were tested. DNase I treatment resulted in dispersal of biofilms, not only in microtiter tray assays but also in flow cell biofilm assays. However, it was also demonstrated that in a culture without eDNA, neither Listeria genomic DNA nor salmon sperm DNA by itself could restore the capacity to adhere. A search for additional necessary components revealed that peptidoglycan (PG), specifically N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), interacted with the DNA in a manner which restored adhesion. If a short DNA fragment (less than approximately 500 bp long) was added to an eDNA-free culture prior to addition of genomic or salmon sperm DNA, adhesion was prevented, indicating that high-molecular-weight DNA is required for adhesion and that the number of attachment sites on the cell surface can be saturated.
Figures


References
-
- Allesen-Holm, M., K. B. Barken, L. Yang, M. Klausen, J. S. Webb, S. Kjelleberg, S. Molin, M. Givskov, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. 2006. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 59:1114-1128. - PubMed
-
- Chae, M. S., and H. Schraft. 2000. Comparative evaluation of adhesion and biofilm formation of different Listeria monocytogenes strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 62:103-111. - PubMed
-
- Costerton, J. W., P. S. Stewart, and E. P. Greenberg. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318-1322. - PubMed
-
- Dell'Anno, A., and R. Danovaro. 2005. Extracellular DNA plays a key role in deep-sea ecosystem functioning. Science 309:2179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

