Factors affecting wound healing
- PMID: 20139336
- PMCID: PMC2903966
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034509359125
Factors affecting wound healing
Abstract
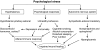
Wound healing, as a normal biological process in the human body, is achieved through four precisely and highly programmed phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. For a wound to heal successfully, all four phases must occur in the proper sequence and time frame. Many factors can interfere with one or more phases of this process, thus causing improper or impaired wound healing. This article reviews the recent literature on the most significant factors that affect cutaneous wound healing and the potential cellular and/or molecular mechanisms involved. The factors discussed include oxygenation, infection, age and sex hormones, stress, diabetes, obesity, medications, alcoholism, smoking, and nutrition. A better understanding of the influence of these factors on repair may lead to therapeutics that improve wound healing and resolve impaired wounds.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn C, Mulligan P, Salcido RS. (2008). Smoking—the bane of wound healing: biomedical interventions and social influences. Adv Skin Wound Care 21:227-238 - PubMed
-
- Anaya DA, Dellinger EP. (2006). The obese surgical patient: a susceptible host for infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 7:473-480 - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Barbul A. (2006). Nutrition and wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(7 Suppl):42S-58S - PubMed
-
- Balaji SM. (2008). Tobacco smoking and surgical healing of oral tissues: a review. Indian J Dent Res 19:344-348 - PubMed
-
- Bishop A. (2008). Role of oxygen in wound healing. J Wound Care 17:399-402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

