Ume6 is required for the MATa/MATalpha cellular identity and transcriptional silencing in Kluyveromyces lactis
- PMID: 20139343
- PMCID: PMC2865933
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.114678
Ume6 is required for the MATa/MATalpha cellular identity and transcriptional silencing in Kluyveromyces lactis
Abstract
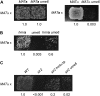
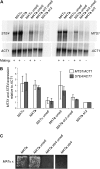
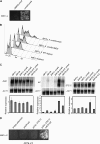
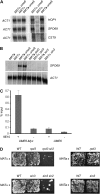
To explore the similarities and differences of regulatory circuits among budding yeasts, we characterized the role of the unscheduled meiotic gene expression 6 (UME6) gene in Kluyveromyces lactis. We found that Ume6 was required for transcriptional silencing of the cryptic mating-type loci HMLalpha and HMRa. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) suggested that Ume6 acted directly by binding the cis-regulatory silencers of these loci. Unexpectedly, a MATa ume6 strain was mating proficient, whereas a MATalpha ume6 strain was sterile. This observation was explained by the fact that ume6 derepressed HMLalpha2 only weakly, but derepressed HMRa1 strongly. Consistently, two a/alpha-repressed genes (MTS1 and STE4) were repressed in the MATalpha ume6 strain, but were expressed in the MATa ume6 strain. Surprisingly, ume6 partially suppressed the mating defect of a MATa sir2 strain. MTS1 and STE4 were repressed in the MATa sir2 ume6 double-mutant strain, indicating that the suppression acted downstream of the a1/alpha2-repressor. We show that both STE12 and the MATa2/HMRa2 genes were overexpressed in the MATa sir2 ume6 strain. Consistent with the idea that this deregulation suppressed the mating defect, ectopic overexpression of Ste12 and a2 in a MATa sir2 strain resulted in efficient mating. In addition, Ume6 served as a block to polyploidy, since ume6/ume6 diploids mated as pseudo a-strains. Finally, Ume6 was required for repression of three meiotic genes, independently of the Rpd3 and Sin3 corepressors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Kluyveromyces lactis Sir2p regulates cation sensitivity and maintains a specialized chromatin structure at the cryptic alpha-locus.Genetics. 2000 Sep;156(1):81-91. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.1.81. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10978277 Free PMC article.
-
The Sir2-Sum1 complex represses transcription using both promoter-specific and long-range mechanisms to regulate cell identity and sexual cycle in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis.PLoS Genet. 2009 Nov;5(11):e1000710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000710. Epub 2009 Nov 6. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19893609 Free PMC article.
-
The KlSTE2 and KlSTE3 genes encode MATalpha- and MATa-specific G-protein-coupled receptors, respectively, which are required for mating of Kluyveromyces lactis haploid cells.Yeast. 2007 Jan;24(1):17-25. doi: 10.1002/yea.1432. Yeast. 2007. PMID: 17192853
-
Transcriptional regulation of meiosis in budding yeast.Int Rev Cytol. 2003;224:111-71. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(05)24004-4. Int Rev Cytol. 2003. PMID: 12722950 Review.
-
Mating-type Gene Switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0013-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0013-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104712 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between Improved Mating Efficiency and Weakened Scaffold-Kinase Interaction in the Mating Pheromone Response Pathway Revealed by Interspecies Complementation.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 14;13:865829. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.865829. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495719 Free PMC article.
-
Linking replication stress with heterochromatin formation.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(3):523-33. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0545-6. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26511280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The duplicated deacetylases Sir2 and Hst1 subfunctionalized by acquiring complementary inactivating mutations.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(16):3351-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05175-11. Epub 2011 Jun 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21690292 Free PMC article.
-
Tight protein-DNA interactions favor gene silencing.Genes Dev. 2011 Jul 1;25(13):1365-70. doi: 10.1101/gad.611011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21724830 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and Functional Trajectory of Sir1 in Gene Silencing.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jan 25;36(7):1164-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01013-15. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26811328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., 1999. Short Protocols in Molecular Biology: A Compendium of Methods From Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
-
- Bahler, J., J. Q. Wu, M. S. Longtine, N. G. Shah, A. McKenzie, III et al., 1998. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14 943–951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

