Preferential expression of MUC6 in oncocytic and pancreatobiliary types of intraductal papillary neoplasms highlights a pyloropancreatic pathway, distinct from the intestinal pathway, in pancreatic carcinogenesis
- PMID: 20139757
- PMCID: PMC3160822
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181cf8bb6
Preferential expression of MUC6 in oncocytic and pancreatobiliary types of intraductal papillary neoplasms highlights a pyloropancreatic pathway, distinct from the intestinal pathway, in pancreatic carcinogenesis
Abstract
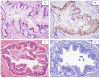
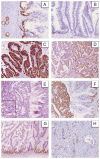
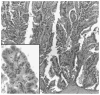
The expression of different MUC glycoproteins has helped define cellular lineage in variety of pancreatic neoplasms, and has helped identify distinct carcinogenic pathways such as the intestinal pathway characterized by diffuse/strong MUC2/CDX2 expression in intestinal-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) and their associated colloid carcinomas (CCs). In this study, the expression profile of MUC6, a pyloric-type mucin, was investigated in both preinvasive and invasive pancreatic neoplasia. Florid papillary ("in-situ") components of 9 intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms (IOPNs), 24 IPMNs, and 7 mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs), were analyzed immunohistochemically for MUC6 expression, as were 15 PanINs, 112 usual invasive ductal adenocarcinomas (DAs), and 14 CCs. In PanINs, MUC6 expression was limited to the very early areas of PanIN-1A that typically have pyloric features. Expression was lost in later stages. Similarly, in IOPNs or IPMNs or MCNs, MUC6 expression was detectable in the cystic or flat areas that have pyloric-like histology. However, in the more advanced (papillary) components of these neoplasms, MUC6 expression was mostly limited to the "cuboidal-cell" but was not seen in the "columnar-cell" phenotype: there was diffuse or strong expression in 8/9 IOPN and, relatively weaker but consistent expression in all 6/6 pancreatobiliary-type IPMNs; whereas virtually no expression in villous or intestinal-type IPMNs. The 7/8 gastric or foveolar-type IPMNs were also negative; in the single case with positivity, the labeling was limited to high-grade dysplastic areas. Interestingly, the papillae in MCNs were also mostly negative. Among invasive carcinomas, 39/112 DAs and only 1/14 CC expressed MUC6. In DA, the expression did not correlate with survival (P=0.94), or any of the markers of aggressiveness: more than 2-cm tumor size (P=0.76), positive surgical margins (P=0.27), lymph node metastasis (P=0.82), or high grade (P=0.08).
In conclusion: (1) The expression of MUC6 in oncocytic and pancreatobiliary-type neoplasms but not in villous or intestinal-type neoplasms supports the presence of a pyloropancreatic pathway distinct from the MUC2/CDX2 expressing intestinal pathway in intraductal papillary neoplasia. (2) MUC6 expression is present in the earliest (nonpapillary) form of any type of preinvasive neoplasia regardless of whether it is PanIN or IOPN or IPMN or MCN suggesting that these entities may share some characteristics early on, but evolve along divergent pathways as they progress.
Figures

References
-
- Adsay NV, Adair CF, Heffess CS, et al. Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:980–994. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV, Merati K, Andea A, et al. The dichotomy in the preinvasive neoplasia to invasive carcinoma sequence in the pancreas: differential expression of MUC1 and MUC2 supports the existence of two separate pathways of carcinogenesis. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:1087–1095. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV, Merati K, Nassar H, et al. Pathogenesis of colloid (pure mucinous) carcinoma of exocrine organs: coupling of gel-forming mucin (MUC2) production with altered cell polarity and abnormal cell-stroma interaction may be the key factor in the morphogenesis and indolent behavior of colloid carcinoma in the breast and pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:571–578. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV, Merati K, Basturk O, et al. Pathologically and biologically distinct types of epithelium in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: delineation of an “intestinal” pathway of carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:839–848. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa T, Klöppel G, Adsay NV, et al. Classification of types of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: a consensus study. Virchows Archiv. 2005;447:794–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

