Baicalin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activation in PC12 cells
- PMID: 20139896
- PMCID: PMC4002841
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.196
Baicalin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activation in PC12 cells
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether the flavonoid baicalin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced injury by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) activation in PC12 cells.
Methods: The effects of baicalin and the 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton on the changes induced by OGD/recovery or H(2)O(2) (an exogenous reactive oxygen species [ROS]) in green fluorescent protein-5-LOX-transfected PC12 cells were compared.
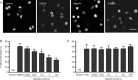
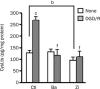
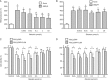
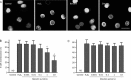
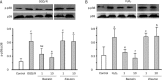
Results: Both baicalin and zileuton attenuated OGD/recovery- and H(2)O(2)-induced injury and inhibited OGD/recovery-induced production of 5-LOX metabolites (cysteinyl leukotrienes) in a concentration-dependent manner. However, baicalin did not reduce baseline cysteinyl leukotriene levels. Baicalin also reduced OGD/recovery-induced ROS production and inhibited 5-LOX translocation to the nuclear envelope and p38 phosphorylation induced by OGD/recovery and H(2)O(2). In contrast, zileuton did not show these effects.
Conclusion: Baicalin can inhibit 5-LOX activation after ischemic injury, which may partly result from inhibition of the ROS/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxygen-glucose deprivation activates 5-lipoxygenase mediated by oxidative stress through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in PC12 cells.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Mar;87(4):991-1001. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21913. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 18951527
-
Baicalin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via inhibiting NMDA receptor-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activation in rat cortical neurons.Pharmacol Res. 2007 Feb;55(2):148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2006.11.007. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Pharmacol Res. 2007. PMID: 17187986
-
Activation of 5-lipoxygenase after oxygen-glucose deprivation is partly mediated via NMDA receptor in rat cortical neurons.J Neurochem. 2006 May;97(4):992-1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03828.x. Epub 2006 Apr 5. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16606359
-
Pranlukast attenuates ischemia-like injury in endothelial cells via inhibiting reactive oxygen species production and nuclear factor-kappaB activation.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;53(1):77-85. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318196736c. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19129732
-
Baicalin and Geniposide Inhibit Polarization and Inflammatory Injury of OGD/R-Treated Microglia by Suppressing the 5-LOX/LTB4 Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jul;46(7):1844-1858. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03305-1. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33891262 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Baicalin Attenuates Ketamine-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Developing Rats: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and CREB/BDNF/Bcl-2 Pathways.Neurotox Res. 2016 Aug;30(2):159-72. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9611-y. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26932180
-
Recent Advances in the Therapeutic Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Baicalin.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 30;14(6):637. doi: 10.3390/biology14060637. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Chinese herbal formula Free and Easy Wanderer ameliorates oxidative stress through KEAP1-NRF2/HO-1 pathway.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11551. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10443-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28912423 Free PMC article.
-
New 3',8''-linked biflavonoids from Selaginella uncinata displaying protective effect against anoxia.Molecules. 2011 Jul 25;16(8):6206-14. doi: 10.3390/molecules16086206. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21788929 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of oxidative stress and 5-lipoxygenase activation by edaravone improves depressive-like behavior after concussion.J Neurotrauma. 2014 Oct 15;31(20):1689-99. doi: 10.1089/neu.2014.3331. Epub 2014 Aug 21. J Neurotrauma. 2014. PMID: 24849726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murphy RC, Gijon MA. Biosynthesis and metabolism of leukotrienes. Biochem J. 2007;405:379–95. - PubMed
-
- Rubin P, Mollison KW. Pharmacotherapy of diseases mediated by 5-lipoxygenase pathway eicosanoids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007;83:188–97. - PubMed
-
- Radmark O, Samuelsson B. 5-lipoxygenase: regulation and possible involvement in atherosclerosis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007;83:162–74. - PubMed
-
- Adamjee J, Suh YJ, Park HS, Choi JH, Penrose JF, Lam BK, et al. Expression of 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase pathway enzymes in nasal polyps of patients with aspirin-intolerant asthma. J Pathol. 2006;209:392–9. - PubMed
-
- Friedman BS, Bel EH, Buntinx A, Tanaka W, Han YH, Shingo S, et al. Oral leukotriene inhibitor (MK-886) blocks allergen-induced airway responses. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:839–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

