CPU86017, a berberine derivative, attenuates cardiac failure through normalizing calcium leakage and downregulated phospholamban and exerting antioxidant activity
- PMID: 20139899
- PMCID: PMC4002834
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.180
CPU86017, a berberine derivative, attenuates cardiac failure through normalizing calcium leakage and downregulated phospholamban and exerting antioxidant activity
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether CPU86017, a berberine derivative, attenuates heart failure by blocking calcium influx and exerting its antioxidant activity.
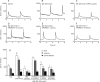
Methods: Myocardial infarction was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats for 17 d followed by isoproterenol (ISO) (5 mg/kg, sc) treatment for 5 d to reduce cardiac function. The rats were divided into 5 groups: sham operation, myocardial infarction (MI), MI plus ISO, and co-treated (in mg/kg, po) with either propranolol (PRO, 10) or CPU86017 (80). Hemodynamic measurements were conducted, and measurements of the redox system, calcium handling proteins and endothelin (ET) system in vivo were done. Furthermore, calcium flux studies and PLB immunocytochemistry were conducted in vitro.
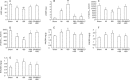
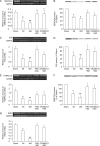
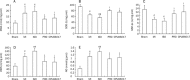
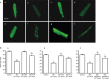
Results: Compared to sham operation, HF was evident following MI and further worsened by ISO treatment. This occurred in parallel with downregulated mRNA and protein production of SERCA2a, PLB, and FKBP12.6, and was associated with upregulation of preproET-1, endothelin converting enzyme, and PKA mRNA production in the myocardium in vivo. Calcium leakage was induced by ISO treatment of isolated beating myocytes in vitro. These changes were attenuated by treatment with either PRO or CPU86017. PLB fluorescence in myocytes was downregulated by ISO treatment, and was relieved significantly by treatment with antioxidant aminoguanidine, ascorbic acid or CPU86017 in vitro.
Conclusion: HF, calcium leakage, downregulated PLB, FKBP12.6, SERCA2a production, and upregulated PKA were caused by ISO treatment, and were abolished by CPU86017 treatment. The beneficial effects of CPU86017 are attributable to its antioxidant and calcium influx blocking effects.
Figures

References
-
- Lehnart SE, Wehrens XH, Kushnir A, Marks AR. Cardiac ryanodine receptor function and regulation in heart disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2004;1015:144–59. - PubMed
-
- Lehnart SE. Novel targets for treating heart and muscle disease: stabilizing ryanodine receptors and preventing intracellular calcium leak. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007;7:225–32. - PubMed
-
- Reiken S, Gaburjakova M, Guatimosim S, Gomez AM, D'Armiento J, Burkhoff D, et al. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of the cardiac calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) in normal and failing hearts. Role of phosphatases and response to isoproterenol. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:444–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

