Chromogranin A is an autoantigen in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 20139986
- PMCID: PMC3166626
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1844
Chromogranin A is an autoantigen in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
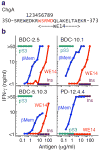
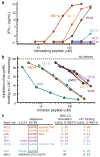
Autoreactive CD4(+) T cells are involved in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases, but the antigens that stimulate their responses have been difficult to identify and in most cases are not well defined. In the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of type 1 diabetes, we have identified the peptide WE14 from chromogranin A (ChgA) as the antigen for highly diabetogenic CD4(+) T cell clones. Peptide truncation and extension analysis shows that WE14 bound to the NOD mouse major histocompatibility complex class II molecule I-A(g7) in an atypical manner, occupying only the carboxy-terminal half of the I-A(g7) peptide-binding groove. This finding extends the list of T cell antigens in type 1 diabetes and supports the idea that autoreactive T cells respond to unusually presented self peptides.
Figures
References
-
- Haskins K. Pathogenic T-cell clones in autoimmune diabetes: more lessons from the NOD mouse. Adv Immunol. 2005;87:123–162. - PubMed
-
- Bergman B, Haskins K. Islet-specific T-cell clones from the NOD mouse respond to β-granule antigen. Diabetes. 1994;43:197–203. - PubMed
-
- Bergman B, McManaman JL, Haskins K. Biochemical characterization of a beta cell membrane fraction antigenic for autoreactive T cell clones. J Autoimmun. 2000;14:343–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10RR023703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U19-AI050864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 DK050561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007405/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK50561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI050864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI17134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI18785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI022295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

