Universal Features for the Classification of Coding and Non-coding DNA Sequences
- PMID: 20140069
- PMCID: PMC2808180
- DOI: 10.4137/bbi.s2236
Universal Features for the Classification of Coding and Non-coding DNA Sequences
Abstract
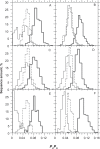
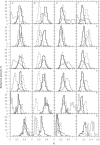
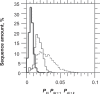
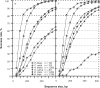
In this report, we revisited simple features that allow the classification of coding sequences (CDS) from non-coding DNA. The spectrum of codon usage of our sequence sample is large and suggests that these features are universal. The features that we investigated combine (i) the stop codon distribution, (ii) the product of purine probabilities in the three positions of nucleotide triplets, (iii) the product of Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine probabilities in 1st, 2nd, 3rd position of triplets, respectively, (iv) the product of G and C probabilities in 1st and 2nd position of triplets. These features are a natural consequence of the physico-chemical properties of proteins and their combination is successful in classifying CDS and non-coding DNA (introns) with a success rate >95% above 350 bp. The coding strand and coding frame are implicitly deduced when the sequences are classified as coding.
Keywords: ancestral codon; coding features; exon prediction; genomics; open reading frame; purine bias.
Figures

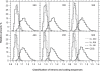
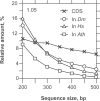
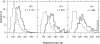
References
-
- Ikehara K, Omori Y, Arai R, et al. A Novel Theory on the Origin of the Genetic Code: A GNC-SNS Hypothesis. J Mol Evol. 2002;54:530–8. - PubMed
-
- Oba T, Fukushima J, Maruyama M, et al. Catalytic activities of [GADV]-peptides. Origins of Life and Evolution of Biospheres. 2005;34:447–60. - PubMed
-
- Musto H, Rodriguez-Maseda H, Bernardi G. Compositional properties of nuclear genes from. Plasmodium falciparum Gene. 1995;152:127–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

