Using Meta-analysis to Compare the Efficacy of Medications for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youths
- PMID: 20140141
- PMCID: PMC2810184
Using Meta-analysis to Compare the Efficacy of Medications for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youths
Abstract
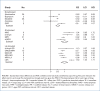
Medications used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have been well researched, but comparisons among agents are hindered by the absence of head-to-head clinical trials. By using meta-analysis, we sought to compare the efficacy of these medications for the symptoms of ADHD. We analyzed published literature on the pharmacotherapy of ADHD to describe the variability of drug-placebo effect sizes and conducted a literature search to identify double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of youths with ADHD that were published after 1979. Meta-analysis regression was used to assess the influence of the medication type on drug effects. We also assessed for publication bias.Thirty-two trials met our criteria and were included in this meta-analysis. These trials involved 16 drugs using 20 different outcome measures of ADHD behaviors. The effect sizes for immediate-release stimulants and long-acting stimulants were similar and were greater than the effect sizes for non-stimulants. There was no evidence of publication bias.Although nearly all of the ADHD medications had significant effects, we found substantial variability. When translated into the costs of treating large numbers of patients, these effect sizes have implications for formulary medication choices.
Keywords: ADHD; efficacy; medications.
Figures
References
-
- Faraone SV, Biederman J. What is the prevalence of adult ADHD? Results of a population screen of 966 adults. J Atten Disord. 2005;9(2):384–391. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet. 2005;366(9481):237–248. - PubMed
-
- Chan E, Zhan C, Homer C.Health care use and costs for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: National estimates from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 20021565(5):504–511. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
