Genetic and functional dissection of HTRA1 and LOC387715 in age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 20140183
- PMCID: PMC2816682
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000836
Genetic and functional dissection of HTRA1 and LOC387715 in age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
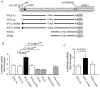
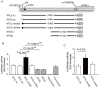
A common haplotype on 10q26 influences the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and encompasses two genes, LOC387715 and HTRA1. Recent data have suggested that loss of LOC387715, mediated by an insertion/deletion (in/del) that destabilizes its message, is causally related with the disorder. Here we show that loss of LOC387715 is insufficient to explain AMD susceptibility, since a nonsense mutation (R38X) in this gene that leads to loss of its message resides in a protective haplotype. At the same time, the common disease haplotype tagged by the in/del and rs11200638 has an effect on the transcriptional upregulation of the adjacent gene, HTRA1. These data implicate increased HTRA1 expression in the pathogenesis of AMD and highlight the importance of exploring multiple functional consequences of alleles in haplotypes that confer susceptibility to complex traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

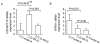
Similar articles
-
Variants in the 10q26 gene cluster (LOC387715 and HTRA1) exhibit enhanced risk of age-related macular degeneration along with CFH in Indian patients.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 May;49(5):1771-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0560. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18436811
-
LOC387715/HTRA1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration: A HuGE review and meta-analysis.Mol Vis. 2010 Oct 5;16:1958-81. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21031019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyses of single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotype linkage of LOC387715 and the HTRA1 gene in exudative age-related macular degeneration in a Chinese cohort.Retina. 2009 Jul-Aug;29(7):974-9. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181a3b90e. Retina. 2009. PMID: 19491722
-
LOC387715/HTRA1 polymorphisms, smoking and combined effects on exudative age-related macular degeneration in a Korean population.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010 Oct;38(7):698-704. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2010.02316.x. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20456446
-
Exploring the contribution of ARMS2 and HTRA1 genetic risk factors in age-related macular degeneration.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023 Nov;97:101159. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2022.101159. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36581531 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and functional dissection of ARMS2 in age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053665. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326481 Free PMC article.
-
Common polymorphisms in angiogenesis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Nov 1;2(11):a006510. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006510. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 23125197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of polymorphisms in CFI and ARMS genes and their association with exudative age-related macular degeneration in Algerian patients.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2022 Jun;11(2):105-111. doi: 10.22099/mbrc.2022.43634.1743. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36059931 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary omega-3 fatty acids, other fat intake, genetic susceptibility, and progression to incident geographic atrophy.Ophthalmology. 2013 May;120(5):1020-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.10.020. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Ophthalmology. 2013. PMID: 23481534 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated C-reactive protein levels and ARMS2/HTRA1 gene variants in subjects without age-related macular degeneration.Mol Vis. 2010 Dec 31;16:2923-30. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21203342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haines JL, Hauser MA, Schmidt S, Scott WK, Olson LM, et al. Complement factor H variant increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration. Science. 2005;308:419–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

