Network-based elucidation of human disease similarities reveals common functional modules enriched for pluripotent drug targets
- PMID: 20140234
- PMCID: PMC2816673
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000662
Network-based elucidation of human disease similarities reveals common functional modules enriched for pluripotent drug targets
Abstract
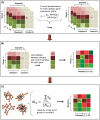
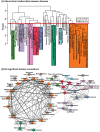
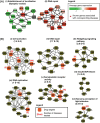
Current work in elucidating relationships between diseases has largely been based on pre-existing knowledge of disease genes. Consequently, these studies are limited in their discovery of new and unknown disease relationships. We present the first quantitative framework to compare and contrast diseases by an integrated analysis of disease-related mRNA expression data and the human protein interaction network. We identified 4,620 functional modules in the human protein network and provided a quantitative metric to record their responses in 54 diseases leading to 138 significant similarities between diseases. Fourteen of the significant disease correlations also shared common drugs, supporting the hypothesis that similar diseases can be treated by the same drugs, allowing us to make predictions for new uses of existing drugs. Finally, we also identified 59 modules that were dysregulated in at least half of the diseases, representing a common disease-state "signature". These modules were significantly enriched for genes that are known to be drug targets. Interestingly, drugs known to target these genes/proteins are already known to treat significantly more diseases than drugs targeting other genes/proteins, highlighting the importance of these core modules as prime therapeutic opportunities.
Conflict of interest statement
Atul J. Butte is or has served as a scientific advisor and/or consultant to NuMedii, Genstruct, Prevendia, Tercica, Eli Lilly and Company, and Johnson & Johnson.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying key genes in rheumatoid arthritis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2017 Aug;20(8):971-979. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13063. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28440025
-
Co-expression analysis reveals key gene modules and pathway of human coronary heart disease.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Feb;119(2):2102-2109. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26372. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28857241
-
Expression-based network biology identifies immune-related functional modules involved in plant defense.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 3;15:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-421. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24888606 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling in drug discovery and development.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 1999 Dec;1(6):671-9. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 1999. PMID: 19629863 Review.
-
Bioinformatics and cancer target discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2004 Sep 15;9(18):795-802. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(04)03224-6. Drug Discov Today. 2004. PMID: 15364067 Review.
Cited by
-
DisSim: an online system for exploring significant similar diseases and exhibiting potential therapeutic drugs.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 26;6:30024. doi: 10.1038/srep30024. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27457921 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Qingkailing ingredients-dependent mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor-axiation "π" structuring module with angiogenesis and neurogenesis effects.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Feb;44(1):35-43. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.01.004. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38213237 Free PMC article.
-
Complex-disease networks of trait-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) unveiled by information theory.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012 Mar-Apr;19(2):295-305. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000482. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012. PMID: 22278381 Free PMC article.
-
Translational bioinformatics: linking the molecular world to the clinical world.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Jun;91(6):994-1000. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2012.49. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22549287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating node embeddings and biological annotations for genes to predict disease-gene associations.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Dec 31;12(Suppl 9):138. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0662-y. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30598097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalaria R. Similarities between Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2002;203–204:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Lage K, Karlberg EO, Storling ZM, Olason PI, Pedersen AG, et al. A human phenome-interactome network of protein complexes implicated in genetic disorders. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Liu Q, Jiang R. Align human interactome with phenome to identify causative genes and networks underlying disease families. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

