Dopaminergic modulation of spiny neurons in the turtle striatum
- PMID: 20140492
- PMCID: PMC11498773
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-010-9499-7
Dopaminergic modulation of spiny neurons in the turtle striatum
Abstract
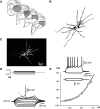
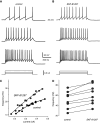
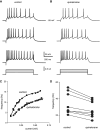
Intracellular recordings were obtained from brain slice preparation in neurons of the striatum of the turtle Trachemys scripta elegans, analogous to the mammalian striatum in its topographic organization, synaptic connectivity, cytoarchitecture, and neurochemistry. Here we show that these similarities extend to the electrophysiological properties of its neurons. Biocytin staining revealed that 85% of the recorded neurons were medium spiny neurons while 15% were aspiny neurons. Spiny neurons of the turtle resembled those found in the mammalian and avian striatum and express dopaminergic D(1) and D(2) class receptors. Because the striatum of the turtle receives a dense dopaminergic innervation from tegmental dopaminergic neurons we investigated the postsynaptic actions of selective dopamine receptor agonists in the excitability of spiny neurons. As in mammals and birds, activation of D(1)-receptors enhances, whereas activation of D(2)-receptors decreases the evoked discharge. Apparently, actions of dopamine agonists occur via the modulation of L-type (Ca(V)1) Ca2+-conductances. Strong cellular evidence suggests that the role of dopamine in the modulation of motor networks is preserved along vertebrate evolution.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen A, Baestrup C, Randrup A (1975) Apomorphine-induced stereotyped biting in the tortoise in relation to dopaminergic mechanisms. Brain Behav Evol 11:365–373 - PubMed
-
- Bargas J, Galarraga E, Aceves J (1989) An early outward conductance modulates the firing latency and frequency of neostriatal neurons of the rat brain. Exp Brain Res 75:146–156 - PubMed
-
- Brauth SE, Reiner A, Kitt CA, Karten HJ (1983) The substance P-containing striato-tegmental path in reptiles: an immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol 219:305–327 - PubMed
-
- Butler A, Hodos W (2005). Comparative vertebrate neuroanatomy, evolution and adaptation, 2nd edn. Wiley Interscience, p 484
-
- Carrillo-Reid L, Tecuapetla F, Tapia D, Hernandez-Cruz A, Galarraga E, Drucker-Colin R, Bargas J (2008) Encoding network states by striatal cell assemblies. J Neurophysiol 99:1435–1450 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

