A comparison of echocardiography to invasive measurement in the evaluation of pulmonary arterial hypertension in a rat model
- PMID: 20140524
- PMCID: PMC2868165
- DOI: 10.1007/s10554-010-9596-1
A comparison of echocardiography to invasive measurement in the evaluation of pulmonary arterial hypertension in a rat model
Abstract
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening condition characterized by progressive elevation in pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) and total pulmonary vascular resistance (TPVR). Recent advances in imaging techniques have allowed the development of new echocardiographic parameters to evaluate disease progression. However, there are no reports comparing the diagnostic performance of these non-invasive parameters to each other and to invasive measurements. Therefore, we investigated the diagnostic yield of echocardiographically derived TPVR and Doppler parameters of PAP in screening and measuring the severity of PAH in a rat model. Serial echocardiographic and invasive measurements were performed at baseline, 21 and 35 days after monocrotaline-induction of PAH. The most challenging echocardiographic derived TPVR measurement had good correlation with the invasive measurement (r = 0.92, P < 0.001) but also more simple and novel parameters of TPVR were found to be useful although the non-invasive TPVR measurement was feasible in only 29% of the studies due to lack of sufficient tricuspid valve regurgitation. However, echocardiographic measures of PAP, pulmonary artery flow acceleration time (PAAT) and deceleration (PAD), were measurable in all animals, and correlated with invasive PAP (r = -0.74 and r = 0.75, P < 0.001 for both). Right ventricular thickness and area correlated with invasive PAP (r = 0.59 and r = 0.64, P < 0.001 for both). Observer variability of the invasive and non-invasive parameters was low except in tissue-Doppler derived isovolumetric relaxation time. These non-invasive parameters may be used to replace invasive measurements in detecting successful disease induction and to complement invasive data in the evaluation of PAH severity in a rat model.
Figures

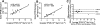
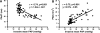
Comment in
-
Evaluation of pulmonary arterial hypertension: invasive or noninvasive?Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Oct;27(7):943-5. doi: 10.1007/s10554-010-9642-z. Epub 2010 May 17. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20473785 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Simonneau G, Robbins IM, Beghetti M, Channick RN, Delcroix M, Denton CP, Elliott CG, Gaine SP, Gladwin MT, Jing ZC, Krowka MJ, Langleben D, Nakanishi N, Souza R. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:S43–S54. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- D’Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, Fishman AP, Goldring RM, Groves BM, Kernis JT. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European society of cardiology (ESC) and the European respiratory society (ERS), endorsed by the International society of heart and lung transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2493–2537. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

