MicroRNAs in cardiac development
- PMID: 20140609
- PMCID: PMC2836460
- DOI: 10.1007/s00246-010-9639-3
MicroRNAs in cardiac development
Abstract
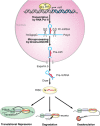
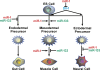
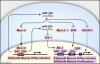
The transcriptional regulation of cardiovascular development requires precise spatiotemporal control of gene expression, and heterozygous mutations of transcription factors have frequently been implicated in human cardiovascular malformations. A novel mechanism involving post-transcriptional regulation by small, noncoding microRNAs (miRNAs) has emerged as a central regulator of many cardiogenic processes. We are beginning to understand the functions that miRNAs play during essential biologic processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, stress response, and tumorigenesis. The identification of miRNAs expressed in specific cardiac and vascular cell types has led to the discovery of important regulatory roles for these small RNAs during cardiomyocyte differentiation, cell cycle, conduction, and vessel formation. Here, we overview the recent findings on miRNA regulation in cardiovascular development. Further analysis of miRNA function during cardiovascular development will allow us to determine the potential for novel miRNA-based therapeutic strategies.
Figures