Effect of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor targeted therapy on chemotherapy in human cancer and the mechanisms involved
- PMID: 20140624
- PMCID: PMC11827821
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0792-0
Effect of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor targeted therapy on chemotherapy in human cancer and the mechanisms involved
Abstract
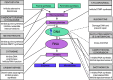
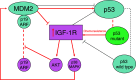
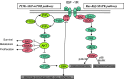
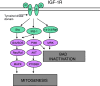
Introduction: Chemotherapy is administered only to patients with advanced cancers, typically to modest avail. Hence, the search for innovative approaches to treat cancer is growing rapidly. One such approach involves targeting molecular pathways identified as encouraging tumor growth and maintenance, particularly the type 1 insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and its receptor (IGF-1R) pathway that is important in conferring chemoresistance.
Materials and methods: This study focuses on IGF-1R targeted therapy, which will enhance chemotherapy efficacy, through reviewing recent literature from PubMed and Medline databases.
Conclusion: This review examines data and strategies addressing an approach conquering chemoresistance through the combination of IGF-1R targeted therapy and chemotherapy in cancer patients, as well as the mechanisms by which IGF-1R acts as a target. This will impact on future research on treatment selection, thereby improving patient prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Molecular-targeted first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 19;7(7):CD011461. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011461.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27432490 Free PMC article.
-
An update on cancer stem cell survival pathways involved in chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Mar;21(6):715-735. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2461443. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39936282 Review.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of IGF1R gene expression in patients with Stage II/III gastric cancer who receive curative surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb;142(2):415-22. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2039-6. Epub 2015 Sep 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26337161 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of common and distinctive mechanisms of resistance to different anti-IGF-IR agents in Ewing's sarcoma.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;26(9):1603-16. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1142. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22798295 Free PMC article.
-
Marginal effects of glucose, insulin and insulin-like growth factor on chemotherapy response in endothelial and colorectal cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2014 Feb;7(2):311-320. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1710. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24396438 Free PMC article.
-
Can we unlock the potential of IGF-1R inhibition in cancer therapy?Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Oct;40(9):1096-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25123819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of doxorubicin cytotoxicity of human cancer cells by tyrosine kinase inhibition of insulin receptor and type I IGF receptor.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):117-26. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1713-x. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21850397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelini A, Iezzi M, Di Febbo C, Di Ilio C, Cuccurullo F, Porreca E (2008) Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in human sarcoma MES-SA/Dx-5 cells by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Oncol Rep 20:731–735 - PubMed
-
- Arora A, Scholar EM (2005) Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeutics 315:971–979 - PubMed
-
- Atzori F, Tabernero J, Cervantes A, Botero M, Hsu K, Brown H et al (2008) A phase I, pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) study of weekly (qW) MK-0646, an insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) monoclonal antibody (MAb) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. ASCO Meet Abstr 26:3519
-
- Bohula EA, Playford MP, Macaulay VM (2003) Targeting the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor as anti-cancer treatment. Anticancer Drugs 14:669–682 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

