Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in BER and HRR genes, XRCC1 haplotypes and breast cancer risk in Caucasian women
- PMID: 20140625
- PMCID: PMC11828125
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0791-1
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in BER and HRR genes, XRCC1 haplotypes and breast cancer risk in Caucasian women
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to assess whether haplotypes in XRCC1 and SNPs in OGG1 and XRCC3 were associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer (BC) and early adverse reactions after radiotherapy.
Methods: 43 Italian breast cancer patients and 31 healthy controls were genotyped for XRCC1(-77T-->C,194,399), OGG1-326 and XRCC3-241 by RFLP-PCR.
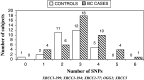
Results: XRCC1-77T-->C, XRCC1-194, OGG1 and XRCC3 were not associated with BC. On the contrary, we found a significant association (p <or= 0.05) between breast cancer occurrence and XRCC1-399. The haplotype (H3) containing the variant allele at codon 399, together with variant C allele in the promoter and wild-type G allele at codon 194 was associated with higher BC risk [p = 0.009, OR = 7.04(1.63-30)]. The probability for developing this tumor was also increased by the number of SNPs in different genes. We found a significantly higher BC risk in subjects with >or=3 SNPs [OR = 2.72 (0.99-7.39), p = 0.04].
Conclusion: In our study, the 399-Gln allele of XRCC1 increased significantly the risk of BC and it may act as a dominant allele [Arg/Arg vs. (Gln/Gln + Arg/Gln), OR = 4.67 (95% CI 1.65-13.23), p = 0.005]. The combination of variant alleles at codon 399 and in position -77 could affect XRCC1 protein activity, impairing genome integrity and promoting cancer occurrence. Also, the number of SNPs in several genes involved in BER and HRR mechanisms made higher the risk of sporadic BC. We can conclude that genetic variants in multiple repair pathways may have a joint or additive effect in cancer risk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between polymorphisms in genes related to DNA base-excision repair with risk and prognosis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Sep;142(9):1917-26. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2202-8. Epub 2016 Jul 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27372710 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 7;26(13):6540. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136540. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650316 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in Base Excision Repair Genes and Association with Multiple Sclerosis in a Pilot Study on a Central European Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 10;26(14):6612. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146612. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724862 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of DNA polymorphisms in key DNA base excision repair proteins on cancer risk.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2012 Oct;31(10):981-1005. doi: 10.1177/0960327112444476. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 23023028 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1) genetic polymorphisms and cervical cancer risk: a huge systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44441. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044441. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984511 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between polymorphisms of XRCC1, p53 and MDR1 genes, the expression of their protein products and prognostic significance in human breast cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2011 Dec;17(12):BR354-63. doi: 10.12659/msm.882121. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 22129893 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms of the XRCC1 gene and breast cancer risk in the Mexican population.Fam Cancer. 2015 Sep;14(3):349-54. doi: 10.1007/s10689-015-9787-y. Fam Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25690738
-
Influence of XRCC1 Genetic Polymorphisms on Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Repair.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Jul 25;2010:780369. doi: 10.4061/2010/780369. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20798883 Free PMC article.
-
Association between OGG1 Ser326Cys and APEX1 Asp148Glu polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Jun 3;9:108. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-108. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24893568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The region of XRCC1 which harbours the three most common nonsynonymous polymorphic variants, is essential for the scaffolding function of XRCC1.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Apr 1;11(4):357-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22281126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreassen CN, Alsner J, Overgaard M, Overgaard J (2003) Prediction of normal tissue radiosensitivity from polymorphisms in candidate genes. Radiother Oncol 69:127–135 - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK, Ear U, Bhattacharyya A et al (1998) Xrcc3 is required for assembly of Rad51 complexes in vivo. J Biol Chem 273:21482–21488 - PubMed
-
- Breast Cancer Association Consortium (2006) Commonly studied single-nucleotide polymorphisms and breast cancer: results from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1382–1396 - PubMed
-
- Brem R, Cox DG, Chapot B et al (2006) The XRCC1−77T→C variant: haplotypes, breast cancer risk, response to radiotherapy and the cellular response to DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 27:2469–2474 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials