Lipopolysaccharide induces calcitonin gene-related peptide in the RAW264.7 macrophage cell line
- PMID: 20141542
- PMCID: PMC2913219
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03239.x
Lipopolysaccharide induces calcitonin gene-related peptide in the RAW264.7 macrophage cell line
Abstract
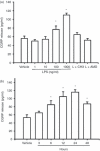
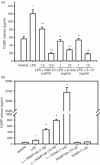
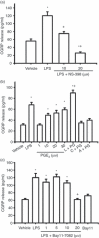
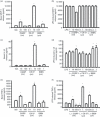
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is widely distributed and plays important roles in a wide array of biological functions. It is enriched in primary sensory neurons and hence involved in nociception and neurogenic inflammation. Recent studies have shown that CGRP can be produced by immune cells such as monocytes/macrophages following inflammatory stimulation, suggesting a role in innate immunity. However, it is unclear how CGRP is up-regulated in macrophages and if it plays a role in macrophage functions such as the production of cytokines and chemokines. Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and multiplex ELISA, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was found to induce CGRP in the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line. LPS-induced inflammatory mediators such as nerve growth factor (NGF), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signalling are involved in inducing CGRP, whereas the NGF receptor trkA and CGRP receptor signalling pathways are unexpectedly involved in suppressing LPS-induced CGRP, which leads to the fine-tune regulation of CGRP release. Exogenous CGRP and CGRP receptor antagonists, in a concentration-dependent manner, stimulated, inhibited or had no effect on basal or LPS-induced release of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, IL-1beta, IL-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and IL-10 in RAW macrophages. The ligand-concentration-dependent regulation of the production of inflammatory mediators by CGRP receptor signalling is a novel mechanism underlying the stimulating and suppressing role of CGRP in immune and inflammatory responses. Together, our data suggest that monocytes/macrophages are an important source of CGRP. Inflammation-induced CGRP has a positive or negative reciprocal effect on the production of other pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. Thereby CGRP plays both facilitating and suppressing roles in immune and inflammatory responses.
Figures
References
-
- Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982;298:240–4. - PubMed
-
- Brain SD, Grant AD. Vascular actions of calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:903–34. - PubMed
-
- Jacques D, Dumont Y, Quirion R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), amylin, and adrenomedullin: anatomical localization and biological functions in the mammalian and human brains. In: Quirion R, Bjorklund A, Hokfelt T, editors. Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2000. pp. 301–56.
-
- van Rossum D, Hanisch UK, Quirion R. Neuroanatomical localization, pharmacological characterization and functions of CGRP, related peptides and their receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1997;21:649–78. - PubMed
-
- Amara SG, Arriza JL, Leff SE, Swanson LW, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG. Expression in brain of a messenger RNA encoding a novel neuropeptide homologous to calcitonin gene-related peptide. Science. 1985;229:1094–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

