FoxO-mediated defense against oxidative stress in osteoblasts is indispensable for skeletal homeostasis in mice
- PMID: 20142101
- PMCID: PMC2819984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.12.009
FoxO-mediated defense against oxidative stress in osteoblasts is indispensable for skeletal homeostasis in mice
Abstract
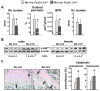
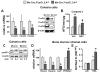
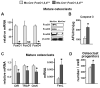
Aging increases oxidative stress and osteoblast apoptosis and decreases bone mass, whereas forkhead box O (FoxO) transcription factors defend against oxidative stress by activating genes involved in free radical scavenging and apoptosis. Conditional deletion of FoxO1, FoxO3, and FoxO4 in 3-month-old mice resulted in an increase in oxidative stress in bone and osteoblast apoptosis and a decrease in the number of osteoblasts, the rate of bone formation, and bone mass at cancellous and cortical sites. The effect of the deletion on osteoblast apoptosis was cell autonomous and resulted from oxidative stress. Conversely, overexpression of a FoxO3 transgene in mature osteoblasts decreased oxidative stress and osteoblast apoptosis and increased osteoblast number, bone formation rate, and vertebral bone mass. We conclude that FoxO-dependent oxidative defense provides a mechanism to handle the oxygen free radicals constantly generated by the aerobic metabolism of osteoblasts and is thereby indispensable for bone mass homeostasis.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, O'Brien CA, Manolagas SC. Oxidative stress antagonizes Wnt signaling in osteoblast precursors by diverting beta-catenin from T cell factor- to forkhead box O-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem. 2007a;282:27298–27305. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, Plotkin LI, Stewart SA, Roberson PK, Kousteni S, O'Brien CA, Bellido T, Parfitt AM, Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Manolagas SC. Skeletal involution by age-associated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem. 2007b;282:27285–27297. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

