Select spinal lesions reveal multiple ascending pathways in the rat conveying input from the male genitalia
- PMID: 20142271
- PMCID: PMC2852996
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.186544
Select spinal lesions reveal multiple ascending pathways in the rat conveying input from the male genitalia
Abstract
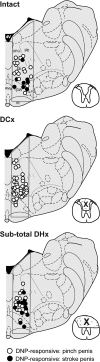
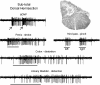
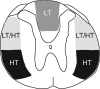
The specific white matter location of all the spinal pathways conveying penile input to the rostral medulla is not known. Our previous studies using rats demonstrated the loss of low but not high threshold penile inputs to medullary reticular formation (MRF) neurons after acute and chronic dorsal column (DC) lesions of the T8 spinal cord and loss of all penile inputs after lesioning the dorsal three-fifths of the cord. In the present study, select T8 lesions were made and terminal electrophysiological recordings were performed 45-60 days later in a limited portion of the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (Gi) and Gi pars alpha. Lesions included subtotal dorsal hemisections that spared only the lateral half of the dorsal portion of the lateral funiculus on one side, dorsal and over-dorsal hemisections, and subtotal transections that spared predominantly just the ventromedial white matter. Electrophysiological data for 448 single unit recordings obtained from 32 urethane-anaesthetized rats, when analysed in groups based upon histological lesion reconstructions, revealed (1) ascending bilateral projections in the dorsal, dorsolateral and ventrolateral white matter of the spinal cord conveying information from the male external genitalia to MRF, and (2) ascending bilateral projections in the ventrolateral white matter conveying information from the pelvic visceral organs (bladder, descending colon, urethra) to MRF. Multiple spinal pathways from the penis to the MRF may correspond to different functions, including those processing affective/pleasure/motivational, nociception, and mating-specific (such as for erection and ejaculation) inputs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of acute and chronic midthoracic spinal cord injury on neural circuits for male sexual function. I. Ascending pathways.J Neurophysiol. 1999 Sep;82(3):1381-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.3.1381. J Neurophysiol. 1999. PMID: 10482756
-
Effects of acute and chronic midthoracic spinal cord injury on neural circuits for male sexual function. II. Descending pathways.J Neurophysiol. 2000 May;83(5):2508-18. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.5.2508. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10805652
-
Responses of medullary reticular formation neurons to input from the male genitalia.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Oct;76(4):2474-82. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.4.2474. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8899620
-
Descending pathways modulating the spinal circuitry for ejaculation: effects of chronic spinal cord injury.Prog Brain Res. 2006;152:415-26. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(05)52028-4. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16198717 Review.
-
Ascending spinal pathways from sexual organs: effects of chronic spinal lesions.Prog Brain Res. 2006;152:401-14. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(05)52027-2. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16198716 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of spinal manipulation thrust duration on trunk mechanical activation thresholds of nociceptive-specific lateral thalamic neurons.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014 Oct;37(8):552-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 12. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25220757 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral bulbospinal projections to pudendal motoneuron circuitry after chronic spinal cord hemisection injury as revealed by transsynaptic tracing with pseudorabies virus.J Neurotrauma. 2011 Apr;28(4):595-605. doi: 10.1089/neu.2009.1180. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Neurotrauma. 2011. PMID: 21265606 Free PMC article.
-
Testing sensation of gently squeezing the testes has diagnostic value in spinal cord injury men.Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2021 Jul 30;7(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41394-021-00430-5. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2021. PMID: 34330888 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of spinal manipulation thrust magnitude on trunk mechanical activation thresholds of lateral thalamic neurons.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014 Jun;37(5):277-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2014.04.001. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24928636 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lateral funiculus sparing, spinal lesion level, and gender on recovery of bladder voiding reflexes and hematuria in rats.J Neurotrauma. 2015 Feb 1;32(3):200-8. doi: 10.1089/neu.2013.3247. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Neurotrauma. 2015. PMID: 25137571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Chaer ED, Lawand NB, Westlund KN, Willis WD. Visceral nociceptive input into the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus: a new function for the dorsal column pathway. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76:2661–2674. - PubMed
-
- Allard J, Truitt WA, McKenna KE, Coolen LM. Spinal cord control of ejaculation. World J Urol. 2005;23:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Altschuler SM, Bao XM, Bieger D, Hopkins DA, Miselis RR. Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J Comp Neurol. 1989;283:248–268. - PubMed
-
- Altschuler SM, Ferenci DA, Lynn RB, Miselis RR. Representation of the cecum in the lateral dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve and commissural subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii in rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991;304:261–274. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KD. Targeting recovery: priorities of the spinal cord-injured population. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:1371–1383. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

