SOLO: a meiotic protein required for centromere cohesion, coorientation, and SMC1 localization in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 20142422
- PMCID: PMC2819681
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904040
SOLO: a meiotic protein required for centromere cohesion, coorientation, and SMC1 localization in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
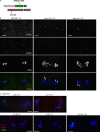
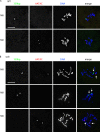
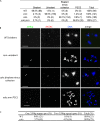
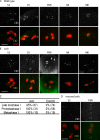
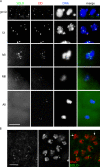
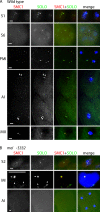
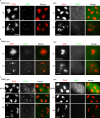
Sister chromatid cohesion is essential to maintain stable connections between homologues and sister chromatids during meiosis and to establish correct centromere orientation patterns on the meiosis I and II spindles. However, the meiotic cohesion apparatus in Drosophila melanogaster remains largely uncharacterized. We describe a novel protein, sisters on the loose (SOLO), which is essential for meiotic cohesion in Drosophila. In solo mutants, sister centromeres separate before prometaphase I, disrupting meiosis I centromere orientation and causing nondisjunction of both homologous and sister chromatids. Centromeric foci of the cohesin protein SMC1 are absent in solo mutants at all meiotic stages. SOLO and SMC1 colocalize to meiotic centromeres from early prophase I until anaphase II in wild-type males, but both proteins disappear prematurely at anaphase I in mutants for mei-S332, which encodes the Drosophila homologue of the cohesin protector protein shugoshin. The solo mutant phenotypes and the localization patterns of SOLO and SMC1 indicate that they function together to maintain sister chromatid cohesion in Drosophila meiosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sisters unbound is required for meiotic centromeric cohesion in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2014 Nov;198(3):947-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.166009. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25194162 Free PMC article.
-
The cohesion protein SOLO associates with SMC1 and is required for synapsis, recombination, homolog bias and cohesion and pairing of centromeres in Drosophila Meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(7):e1003637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003637. Epub 2013 Jul 18. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23874232 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and regulation of the Drosophila centromere cohesion protein MEI-S332 family.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Mar 29;360(1455):543-52. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1619. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15915585 Free PMC article.
-
Shugoshin protects cohesin complexes at centromeres.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Mar 29;360(1455):515-21, discussion 521. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1607. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15897177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shugoshins: from protectors of cohesion to versatile adaptors at the centromere.Trends Genet. 2012 Jul;28(7):351-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Trends Genet. 2012. PMID: 22542109 Review.
Cited by
-
Homolog pairing and sister chromatid cohesion in heterochromatin in Drosophila male meiosis I.Chromosoma. 2011 Aug;120(4):335-51. doi: 10.1007/s00412-011-0314-0. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Chromosoma. 2011. PMID: 21384262
-
Sisters unbound is required for meiotic centromeric cohesion in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2014 Nov;198(3):947-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.166009. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25194162 Free PMC article.
-
Meiosis in male Drosophila.Spermatogenesis. 2012 Jul 1;2(3):167-184. doi: 10.4161/spmg.21800. Spermatogenesis. 2012. PMID: 23087836 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of a Novel Mitochondrially-Encoded Gene in Gonadic Precursors May Drive Paternal Inheritance of Mitochondria.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 4;10(9):e0137468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137468. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26339998 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of centromere localization of the Drosophila Shugoshin MEI-S332 and sister-chromatid cohesion in meiosis.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Jul 31;4(10):1849-58. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.012823. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 25081981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner M., Thompson P., Roote J., Lasko P.F., Grau Y., el Messal M., Roth S., Simpson P. 1990. The genetics of a small autosomal region of Drosophila melanogaster containing the structural gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. VII. Characterization of the region around the snail and cactus loci. Genetics. 126:679–694 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

