Trends in incidence, severity, and outcome of hospitalized myocardial infarction
- PMID: 20142444
- PMCID: PMC2827641
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.897249
Trends in incidence, severity, and outcome of hospitalized myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: In 2000, the definition of myocardial infarction (MI) changed to rely on troponin rather than creatine kinase (CK) and its MB fraction (CK-MB). The implications of this change on trends in MI incidence and outcome are not defined.
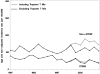
Methods and results: This was a community study of 2816 patients hospitalized with incident MI from 1987 to 2006 in Olmsted County, Minnesota, with prospective measurements of troponin and CK-MB from August 2000 forward. Outcomes were MI incidence, severity, and survival. After troponin was introduced, 278 (25%) of 1127 incident MIs met only troponin-based criteria. When cases meeting only troponin criteria were included, incidence did not change between 1987 and 2006. When restricted to cases defined by CK/CK-MB, the incidence of MI declined by 20%. The incidence of non-ST-segment elevation MI increased markedly by relying on troponin, whereas that of ST-segment elevation MI declined regardless of troponin. The age- and sex-adjusted hazard ratio of death within 30 days for an infarction occurring in 2006 (compared with 1987) was 0.44 (95% confidence interval, 0.30 to 0.64). Among 30-day survivors, survival did not improve, but causes of death shifted from cardiovascular to noncardiovascular (P=0.001). Trends in long-term survival among 30-day survivors were similar regardless of troponin.
Conclusions: Over the last 2 decades, a substantial change in the epidemiology of MI occurred that was only partially mediated by the introduction of troponin. Non-ST-segment elevation MIs now constitute the majority of MIs. Although the 30-day case fatality improved markedly, long-term survival did not change, and the cause of death shifted from cardiovascular to noncardiovascular.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

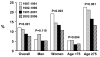
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O'Donnell C, Roger V, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wilson M, Hong Y. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–146. - PubMed
-
- Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined--a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:959–969. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Tanasijevic MJ, Thompson B, Schactman M, McCabe CH, Cannon CP, Fischer GA, Fung AY, Thompson C, Wybenga D, Braunwald E. Cardiac-specific troponin I levels to predict the risk of mortality in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1342–1349. - PubMed
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H. Redefinition of myocardial infarction by a consensus dissenter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:1472–1474. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Jaffe AS, Apple FS, Galvani M, Katus HA, Newby LK, Ravkilde J, Chaitman B, Clemmensen PM, Dellborg M, Hod H, Porela P, Underwood R, Bax JJ, Beller GA, Bonow R, Van der Wall EE, Bassand JP, Wijns W, Ferguson TB, Steg PG, Uretsky BF, Williams DO, Armstrong PW, Antman EM, Fox KA, Hamm CW, Ohman EM, Simoons ML, Poole-Wilson PA, Gurfinkel EP, Lopez-Sendon JL, Pais P, Mendis S, Zhu JR, Wallentin LC, Fernandez-Aviles F, Fox KM, Parkhomenko AN, Priori SG, Tendera M, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Vahanian A, Camm AJ, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Morais J, Brener S, Harrington R, Morrow D, Lim M, Martinez-Rios MA, Steinhubl S, Levine GN, Gibler WB, Goff D, Tubaro M, Dudek D, Al-Attar N. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;116:2634–2653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

