A cell protection screen reveals potent inhibitors of multiple stages of the hepatitis C virus life cycle
- PMID: 20142494
- PMCID: PMC2840489
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0915117107
A cell protection screen reveals potent inhibitors of multiple stages of the hepatitis C virus life cycle
Abstract
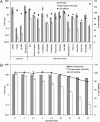
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) life cycle involves multiple steps, but most current drug candidates target only viral replication. The inability to systematically discover inhibitors targeting multiple steps of the HCV life cycle has hampered antiviral development. We present a simple screen for HCV antivirals based on the alleviation of HCV-mediated cytopathic effect in an engineered cell line-n4mBid. This approach obviates the need for a secondary screen to avoid cytotoxic false-positive hits. Application of our screen to 1280 compounds, many in clinical trials or approved for therapeutic use, yielded >200 hits. Of the 55 leading hits, 47 inhibited one or more aspects of the HCV life cycle by >40%. Six compounds blocked HCV entry to levels similar to an antibody (JS-81) targeting the HCV entry receptor CD81. Seven hits inhibited HCV replication and/or infectious virus production by >100-fold, with one (quinidine) inhibiting infectious virus production by 450-fold relative to HCV replication levels. This approach is simple and inexpensive and should enable the rapid discovery of new classes of HCV life cycle inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
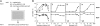
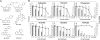
Similar articles
-
Identification of novel anti-hepatitis C virus agents by a quantitative high throughput screen in a cell-based infection assay.Antiviral Res. 2015 Dec;124:20-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26515788 Free PMC article.
-
Novel cell-based hepatitis C virus infection assay for quantitative high-throughput screening of anti-hepatitis C virus compounds.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):995-1004. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02094-13. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24277038 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus complete life cycle screen for identification of small molecules with pro- or antiviral activity.Antiviral Res. 2011 Feb;89(2):136-48. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 21167208
-
[Antiviral agents for analyzing virus life cycle: chemical genetics for virology].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(11):1169-75. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00212-4. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 24189558 Review. Japanese.
-
The history of hepatitis C virus (HCV): Basic research reveals unique features in phylogeny, evolution and the viral life cycle with new perspectives for epidemic control.J Hepatol. 2016 Oct;65(1 Suppl):S2-S21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.035. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27641985 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of 3,4-Dihydro-2H,6H-pyrimido[1,2-c][1,3]benzothiazin-6-imine Derivatives as Novel Selective Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 5;22(13):7236. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137236. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281290 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Piperazinylbenzenesulfonamides as New Inhibitors of Claudin-1 Trafficking and Hepatitis C Virus Entry.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e01982-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01982-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491159 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of the antihistamine chlorcyclizine and related compounds for treatment of hepatitis C virus infection.Sci Transl Med. 2015 Apr 8;7(282):282ra49. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3010286. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25855495 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of Tetraspanin CD81 with Monoclonal Antibodies and Small Molecules to Combat Cancers and Viral Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 6;15(7):2186. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072186. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Dual-reporter system for real-time monitoring and high-throughput CRISPR/Cas9 library screening of the hepatitis C virus.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 9;5:8865. doi: 10.1038/srep08865. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25746010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohmann V, et al. Replication of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science. 1999;285:110–113. - PubMed
-
- Dansako H, et al. A new living cell-based assay system for monitoring genome-length hepatitis C virus RNA replication. Virus Res. 2008;137:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Mondal R, et al. Development of a cell-based assay for high-throughput screening of inhibitors against HCV genotypes 1a and 1b in a single well. Antiviral Res. 2009;82:82–88. - PubMed
-
- Lindenbach BD, et al. Complete replication of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Science. 2005;309:623–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

