Construction and genetic selection of small transmembrane proteins that activate the human erythropoietin receptor
- PMID: 20142506
- PMCID: PMC2840434
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0915057107
Construction and genetic selection of small transmembrane proteins that activate the human erythropoietin receptor
Abstract
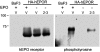
This work describes a genetic approach to isolate small, artificial transmembrane (TM) proteins with biological activity. The bovine papillomavirus E5 protein is a dimeric, 44-amino acid TM protein that transforms cells by specifically binding and activating the platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGFbetaR). We used the E5 protein as a scaffold to construct a retrovirus library expressing approximately 500,000 unique 44-amino acid proteins with randomized TM domains. We screened this library to select small, dimeric TM proteins that were structurally unrelated to erythropoietin (EPO), but specifically activated the human EPO receptor (hEPOR). These proteins did not activate the murine EPOR or the PDGFbetaR. Genetic studies with one of these activators suggested that it interacted with the TM domain of the hEPOR. Furthermore, this TM activator supported erythroid differentiation of primary human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro in the absence of EPO. Thus, we have changed the specificity of a protein so that it no longer recognizes its natural target but, instead, modulates an entirely different protein. This represents a novel strategy to isolate small artificial proteins that affect diverse membrane proteins. We suggest the word "traptamer" for these transmembrane aptamers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mapping the homodimer interface of an optimized, artificial, transmembrane protein activator of the human erythropoietin receptor.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 30;9(4):e95593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095593. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24788775 Free PMC article.
-
The bovine papillomavirus E5 protein and the PDGF beta receptor: it takes two to tango.Virology. 2009 Feb 20;384(2):345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.09.033. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Virology. 2009. PMID: 18990418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Packing contacts can mediate highly specific interactions between artificial transmembrane proteins and the PDGFbeta receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 17;104(29):11945-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704348104. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17609376 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid substitution converts a transmembrane protein activator of the platelet-derived growth factor β receptor into an inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 20;288(38):27273-27286. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470054. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23908351 Free PMC article.
-
The platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor as a target of the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Dec;11(4):283-93. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00012-5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10959076 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-spanning transmembrane domains in cell growth and cell-cell interactions: More than meets the eye?Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Apr-Jun;4(2):313-24. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.2.12430. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20543559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the homodimer interface of an optimized, artificial, transmembrane protein activator of the human erythropoietin receptor.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 30;9(4):e95593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095593. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24788775 Free PMC article.
-
TBC1D5-Catalyzed Cycling of Rab7 Is Required for Retromer-Mediated Human Papillomavirus Trafficking during Virus Entry.Cell Rep. 2020 Jun 9;31(10):107750. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107750. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32521275 Free PMC article.
-
JAK2 activation by growth hormone and other cytokines.Biochem J. 2015 Feb 15;466(1):1-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141293. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25656053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel assay for the detection of anti-human platelet antigen antibodies (HPA-1a) based on peptide aptamer technology.Haematologica. 2012 May;97(5):696-704. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.051276. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22133781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehnert U, et al. Computational analysis of membrane proteins: Genomic occurrence, structure prediction and helix interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 2004;37:121–146. - PubMed
-
- Schlegel R, Wade-Glass M, Rabson MS, Yang Y-C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small hydrophobic protein. Science. 1986;233:464–467. - PubMed
-
- Burkhardt A, Willingham M, Gay C, Jeang K-T, Schlegel R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus is oriented asymmetrically in Golgi and plasma membranes. Virology. 1989;170:334–339. - PubMed
-
- Surti T, Klein O, Aschheim K, DiMaio D, Smith SO. Structural models of the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein. Proteins. 1998;33:601–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

