Phase II trial of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in relapsed or refractory Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- PMID: 20142598
- PMCID: PMC2834498
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.0994
Phase II trial of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in relapsed or refractory Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Abstract
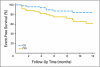
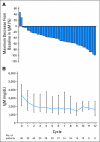
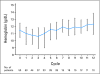
PURPOSE The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signal transduction pathway controls cell proliferation and survival. Everolimus is an oral agent targeting raptor mTOR (mTORC1). The trial's goal was to determine the antitumor activity and safety of single-agent everolimus in patients with relapsed/refractory Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). PATIENTS AND METHODS Eligible patients had measurable disease (immunoglobulin M monoclonal protein > 1,000 mg/dL with > 10% marrow involvement or nodal masses > 2 cm), a platelet count more than 75,000 x 10(6)/L, a neutrophil count more than 1,000 x 10(6)/L, and a creatinine and bilirubin less than 2 x the laboratory upper limit of normal. Patients received everolimus 10 mg orally daily and were evaluated monthly. Tumor response was assessed after cycles 2 and 6 and then every three cycles until progression. Results Fifty patients were treated. The median age was 63 years (range, 43 to 85 years). The overall response rate (complete response plus partial remission [PR] plus minimal response [MR]) was 70% (95% CI, 55% to 82%), with a PR of 42% and 28% MR. The median duration of response and median progression-free survival (PFS) have not been reached. The estimated PFS at 6 and 12 months is 75% (95% CI, 64% to 89%) and 62% (95% CI, 48% to 80%), respectively. Grade 3 or higher related toxicities were observed in 56% of patients. The most common were hematologic toxicities with cytopenias. Pulmonary toxicity occurred in 10% of patients. Dose reductions due to toxicity occurred in 52% of patients. CONCLUSION Everolimus has high single-agent activity with an overall response rate of 70% and manageable toxicity in patients with relapsed WM and offers a potential new therapeutic strategy for this patient group.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
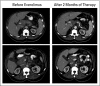
References
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Panayiotidis P, Moulopoulos LA, et al. Waldenström's macroglobulinemia: Clinical features, complications, and management. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:214–226. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Kyle RA, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. Diagnosis and management of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1564–1577. - PubMed
-
- Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: Consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:110–115. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

