Ethnicity-based subgroup meta-analysis of the association of LOXL1 polymorphisms with glaucoma
- PMID: 20142848
- PMCID: PMC2817013
Ethnicity-based subgroup meta-analysis of the association of LOXL1 polymorphisms with glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the association and ethnic heterogeneity of lysyl oxidase-like 1 (LOXL1) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with exfoliation syndrome (XFS)/exfoliation glaucoma (XFG) and other types of glaucoma.
Methods: We performed meta-analysis and ethnicity-based subgroup analyses according to published studies. Allele and genotype frequencies of SNPs rs1048661, rs2165241, and rs3825942 were extracted for analysis in Reviewer Manager: (1) comparison of the allelic distributions between XFS and XFG, (2) allelic association of LOXL1 SNPs with XFS/XFG, (3) associations in homozygote, heterozygote, and dominant and recessive models, and (4) allelic association with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG).
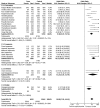
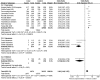
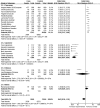
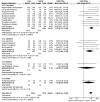
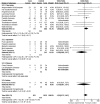
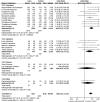
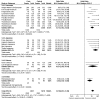
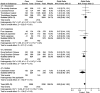
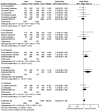
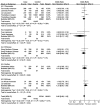
Results: In total 24 reported articles were retrieved, including Caucasian, African, Japanese, Indian, and Chinese populations. There was no significant difference in the distributions of rs1048661, rs2165241, and rs3825942 between XFS and XFG. The G allele of rs3825942 was the common at-risk allele for XFS/XFG in all populations with a total odds ratio (OR) of 10.89. The total homozygote OR of rs3825942 was 9.06 for XFS/XFG combined, but the total heterozygote OR was not significant. We also found that in the recessive model, the total OR was 14.70. There was no association of the three SNPs with POAG.
Conclusions: The association of rs3825942, but not rs2165241 or rs1048661, with XFS/XFG is consistent in different ethnic populations in the recessive model. LOXL1 is not associated with POAG in all study populations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of LOXL1 polymorphisms in exfoliation syndrome in the Uygur population.Mol Vis. 2011;17:1734-44. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21738402 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of LOXL1 gene polymorphisms in exfoliation syndrome and exfoliation glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2008 Mar 17;14:533-41. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18385788 Free PMC article.
-
Association of LOXL1 gene polymorphisms with exfoliation syndrome/glaucoma and primary open angle glaucoma in a Turkish population.Mol Vis. 2013;19:114-20. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23378724 Free PMC article.
-
From epidemiology to lysyl oxidase like one (LOXL1) polymorphisms discovery: phenotyping and genotyping exfoliation syndrome and exfoliation glaucoma in Iceland.Acta Ophthalmol. 2009 Aug;87(5):478-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2009.01635.x. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19664108 Review.
-
Exfoliation Syndrome: A Disease of Autophagy and LOXL1 Proteopathy.J Glaucoma. 2018 Jul;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S44-S53. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000919. J Glaucoma. 2018. PMID: 29547474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of lysyl oxidase-like 1 DNA copy number variants in exfoliation glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2012;18:2976-81. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 23288989 Free PMC article.
-
LOXL1 folding in exfoliation glaucoma.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2019;118:273-288. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31928728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New pathogenetic insights into pseudoexfoliation syndrome/glaucoma. Therapeutically relevant?].Ophthalmologe. 2012 Oct;109(10):944-51. doi: 10.1007/s00347-012-2531-1. Ophthalmologe. 2012. PMID: 23053330 Review. German.
-
Genetics and genomics of pseudoexfoliation syndrome/glaucoma.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2011 Jan;18(1):30-6. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.75882. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21572731 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of LOXL1 polymorphisms in a Saudi Arabian population with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2010 Dec 16;16:2805-10. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21197115 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
