Evaluation of the efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic field in the management of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy
- PMID: 20142869
- PMCID: PMC2812751
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-3930.53121
Evaluation of the efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic field in the management of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy
Abstract
Aim: The study was carried out to evaluate and compare the effect of low power, low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) of 600 and 800 Hz, respectively, in management of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy.
Settings and designs: The study was a randomized controlled trial performed in Guru Nanak Dev University and Medical College, Amritsar, India with different subject experimental design.
Materials and methods: Thirty subjects within an age group of 40-68 years with diabetic polyneuropathy stages N1a, N1b, N2a were randomly allocated to groups 1, 2, 3 with 10 subjects in each. Group 1 and 2 were treated with low power 600 and 800-Hz PEMF for 30 min for 12 consecutive days. Group 3 served as control on usual medical treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN). The subjects with neuropathy due to any cause other than diabetes were excluded. The pain and motor nerve conduction parameters (distal latency, amplitude, nerve conduction velocity) were assessed before and after treatment.
Statistical analysis: Related t-test and unrelated t-test were used for data analysis.
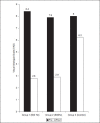
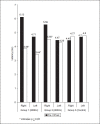
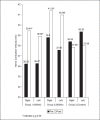
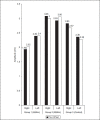
Results: Significant reduction in pain and statistically significant (P<0.05) improvement in distal latency and nerve conduction velocity were seen in experimental group 1 and 2.
Conclusions: Low-frequency PEMF can be used as an adjunct in reducing neuropathic pain as well as for retarding the progression of neuropathy in a short span of time.
Keywords: Diabetic polyneuropathy; nerve conduction velocity; pulsed electromagnetic field.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pulsed electromagnetic fields to reduce diabetic neuropathic pain and stimulate neuronal repair: a randomized controlled trial.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009 Jul;90(7):1102-9. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2009.01.019. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009. PMID: 19577022 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic effects of 15 Hz pulsed electromagnetic field on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-treated rats.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 18;8(4):e61414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061414. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23637830 Free PMC article.
-
EFFECT OF NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE ON THE COURSE OF DIABETIC POLYNEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS.Wiad Lek. 2023;76(11):2395-2400. doi: 10.36740/WLek202311109. Wiad Lek. 2023. PMID: 38112355
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Shuxuetong Injection in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;47(11):3088-3094. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220303.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35718533 Chinese.
-
Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) as an adjunct therapy for pain management in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.Int Urogynecol J. 2022 Mar;33(3):487-491. doi: 10.1007/s00192-021-04862-3. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Int Urogynecol J. 2022. PMID: 34100976 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study of the efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic field and low level laser therapy on mitogen-activated protein kinases.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017 Jan 25;9:316-321. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.01.008. eCollection 2017 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017. PMID: 28956019 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the effects combined physical procedures and alpha-lipoic acid on the electroneurographic parameters of patients with distal sensorimotor diabetic polyneuropathy.J Phys Ther Sci. 2016 Jan;28(2):432-7. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.432. Epub 2016 Feb 29. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016. PMID: 27065527 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effect of separate and simultaneous application of Tecar therapy and low-level laser therapy on the neurological symptoms of type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy of lower limbs.Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024 Aug 26;70(3):344-357. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2024.13419. eCollection 2024 Sep. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 39679116 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Adding Electromagnetic Therapy or Laser Therapy to Medications in Patients With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.J Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Winter;11(1):20-28. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2020.05. Epub 2020 Jan 18. J Lasers Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32099623 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation for Pain Management in the Inpatient Setting: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2021 Mar 15;13(3):e13892. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13892. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33880248 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boulton AJ, Malik RA. Diabetic neuropathy. Med Clin North Am. 1998;82:909–29. - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: A statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:956–62. - PubMed
-
- Vinik AI. Diagnosis and management of diabetic neuropathy. Clin Geriatr Med. 1999;15:293–316. - PubMed
-
- Kotov SV, Kalinin AP, Rudakova IG. Diabetic Neuropathy (in Russian) Meditsina, Moscow: 2000.
-
- Kotov SV, Neretin VYa, Petina LV, Kamynina TS. Clinical and electroneurophysiological studies of the state of the neuromuscular system in patients with diabetes mellitus types I and II. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr. 1997;97:34–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
